Sports and Mental Health
What Is the Connection Between Sports and Mental Health?
Sports participation is associated with several mental health benefits, such as social connections, self-confidence, and an increased sense of connection and belonging.
Additional benefits of sports include a reduced risk of obesity from physical activity and an increase in the feel-good hormone, endorphins.
However, while there are many positive mental health benefits, participating in sports can also lead to mental health challenges, especially in those who are involved in highly competitive sports, such as college and elite athletes.
What Are the Emotional Benefits of Playing Sports?
There are several emotional benefits of playing sports, such as:
- Reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress
- Increased self-esteem
- An improved sense of well-being and quality of life
- Strong social connections, such as a sense of belonging, especially in team sports
Team sports tend to promote the strongest benefits over individual sports.
What Are the Most Common Mental Health Challenges for Athletes?
The most common mental health challenges for athletes include performance anxiety, depression, burnout, eating disorders, substance use, and struggles after injuries.
These issues often stem from high pressure to perform, physical demands, and the player’s identity being tied to their sport.
How Do Stigmas Around Mental Health Affect Athletes?
Many athletes feel pressure to always be tough and in control, but that stigma can make it hard for them to perform well in their sport.
Worries about being judged, losing a spot on the team, or looking “weak” often keep athletes from reaching out for help. Instead, they may push their feelings down, which can make things like stress, anxiety, or depression even worse. Over time, this doesn’t just hurt their mental health, it can also affect how they play, making it harder to focus, recover, or enjoy the sport they love.
Why Do Athletes Struggle With Mental Health?
While there are many benefits to playing sports, competitive athletes face several stressors, such as injuries and intense pressure to perform well.
Collegiate and professional athletes may feel pressure from social media and work-life balance. Athletes may travel a lot during their sport’s season, leaving little time for family and friends outside of practices and games.
Collegiate or student athletes (e.g., those still in high school) may struggle to balance the demands of school alongside their sport.
How Does Mental Health Affect Athletic Performance?
Mental health issues, such as intense anxiety before a game or eating disorders from the pressure to look a certain way, can reduce focus, slow reaction times, or negatively impact motivation.
Just like a physical injury can directly impact athletic performance, so can a mental condition or illness.
What Are Some Key Athlete Mental Health Statistics?
Among athletes, gender, age, competitiveness of the sport, and injuries all impact mental health.
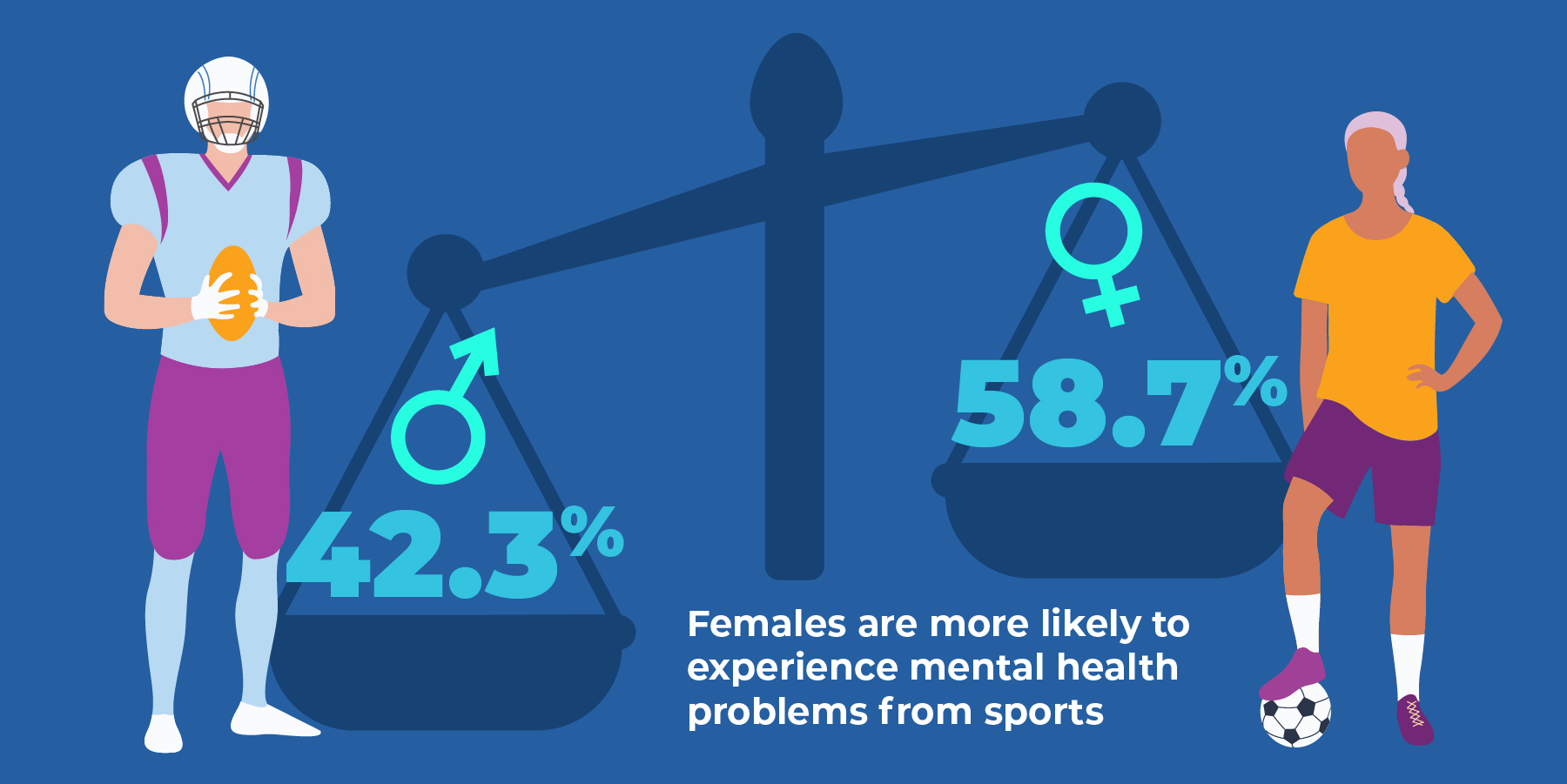
- Differences in sex: Females are more likely to experience mental health problems from sports, but also more likely to seek support. In one study, females had a 58.7% lifetime prevalence of mental health problems compared to their male counterparts, who experienced a lifetime prevalence of 42.3%.
- Mental health problems: In the same study, symptoms of anxiety and depression were the most common mental health problems, with an overall prevalence of 19.5%.
- Highest rates: Among student athletes, women, BIPOC, and LGBTQ+ student athletes reported the highest rates of mental health challenges.
- Risk of burnout: Burnout is a common mental health issue, with some data indicating that 6-11% of athletes are affected. Athletes who are females, later in their careers, or have experienced an injury, may be more likely to experience burnout.
Note: When referring to studies, the language the study uses around sex and gender (e.g., male vs. female, women vs. men) is used when referencing those studies.
What Types of Mental Health Challenges Do Athletes Face?
Athletes face several mental health challenges, ranging from anxiety and performance pressure to an increased risk of physical injuries, such as concussions.
Specific mental health challenges include:
- Anxiety and performance pressure: Competitive environments can create significant stressors. Athletes may experience anxiety and pressure around letting down teammates, losing scholarships, or not playing their best. For student athletes, balancing school and sports can feel overwhelming.
- Depression: Injuries, losing, or retiring from a sport may trigger symptoms of depression in some. Symptoms to watch for include low energy, loss of interest in activities, and feelings of hopelessness. For many, their identity is often tied to their sport and performance, and so setbacks can feel deeply personal.
- Eating disorders and body image concerns: Some sports, such as gymnastics, wrestling, and dance, have a higher emphasis on appearances, and individuals in these sports may be at a higher risk of eating disorders. In wrestling, for example, participants may go to extreme measures to make a particular weight category. The pressure to look a certain way can impact both physical health and emotional well-being.
- Burnout: While sports are a great way to stay active, overtraining, lack of rest, and constant competition can lead to burnout. Feeling burned out is more than being tired—it’s a state of emotional and physical exhaustion.
- Concussion-related mental health problems: While head injuries can affect memory and focus in the short term, they can also make someone more susceptible to several long-term issues, such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
- Substance use: To manage the stress of sports, some athletes turn to alcohol or drugs. Athletes may also use performance-enhancing drugs. Any substance use furthers mental health problems and risks.
- Stigma and identity struggles: Athletes are expected to be tough, and much of an athlete’s identity is wrapped up in their sport. The stigma associated with toughness may make it harder for an athlete to reach out to mental health professionals or access mental health resources.
- Social media pressures: For college athletes and professional athletes, a lot of pressure can come from online criticism, comparisons, and constant visibility. This added stress can add to existing risk factors for mental illness.
Sports Performance Anxiety
What Is Performance Anxiety in Sports?
Performance anxiety occurs when an athlete’s nerves, fear of failure, or external expectations overwhelm them before or during a competition.
Performance anxiety is very common among student athletes. Research suggests that about 30–60% of student athletes experience significant performance anxiety before games or practices.
Many don’t seek help because of stigma or the expectation to be “mentally tough” or “pushing through.”
What Are the Signs That Someone Is Dealing With Competitive Anxiety?
Signs that someone may be dealing with competitive anxiety include:
- Difficulty sleeping before games
- Negative self-talk
- Perfectionist tendencies
- Racing heart and sweaty palms
- Stomachaches
- Avoiding practices and competitions or arriving late
How Does Anxiety Influence Sports Performance?
Anxiety can negatively affect sports performance by causing the athlete to second-guess themselves, freeze up in critical moments, or participate more cautiously.
Additionally, it can erode an athlete’s self-confidence and ability to perform consistently.
How To Deal With Performance Anxiety as a Student Athlete?
There are several strategies to manage performance anxiety as a student athlete, including:
- Talking about it: Sharing your struggles with your coaches, teammates, or a mental health professional can help you process your anxiety and find relief.
- Practicing mindfulness: Learning and practicing grounding strategies, deep breathing, or meditation can help you relax your body and mind.
- Keeping perspective: Remembering that it’s about showing up consistently and doing your best, not being perfect, can reduce pressure and negative self-talk.
- Building daily wellness routines: Focusing on the basics of self-care, such as good sleep, nutrition, and recovery, can help your body be at its best.
Emotional Struggles from Physical Challenges
How Do Sports Injuries Affect Emotional Health?
Sports injuries can lead to frustration, loneliness, and symptoms of depression.
Injuries may cause both physical setbacks that take a toll on emotional health, too, since players feel frustrated and discouraged that they are not performing at the level they used to.
How Do Concussions Impact Mental Health?
Concussions, especially repeated concussions, can increase the risk of mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, or long-term cognitive issues.
Can Getting Injured Make You Scared To Play Sports Again?
Absolutely. Getting injured can make you hesitant or fearful to play sports again.
This fear can make returning to your sport emotionally challenging, even if your body has healed, and lead to performance issues.
For some sports, such as gymnastics, hesitating or “bailing out” can actually increase the risk of getting injured again.
This is part of the reason that injuries are a risk factor for athletes experiencing burnout.
Stress in Athletes
What Causes Stress in Athletes?
There are several causes of stress in athletes, including:
- Academic pressures: High school and college athletes need to balance academics with the rigorous demands of their sport.
- Work-life balance: Many athletes have families, and it can be tough to find a balance between long practices, traveling, and spending time with family.
- Concern over scholarship or roster spots: An athlete may fear losing their place on the team or scholarship if they don’t perform up to a certain standard.
- Social pressure: Social media can fuel stress through comments from the general public and constant comparison.
What Are the Warning Signs That a Student Athlete Is Overstressed?
Signs that a student athlete is overstressed include irritability and mood swings, difficulty concentrating, decreased athletic performance, and physical symptoms such as a headache, stomachache, or fatigue.
What Effects Does Stress Have on Sports Performance?
Chronic stress can have several adverse effects, such as a decrease in energy, reduced ability to focus, and potentially an increased risk of injury.
Additionally, poorly managed stress can eventually lead to burnout or more serious mental health problems.
Can Stress Lead to an Athlete Burning Out?
Yes, while stress can lead to an athlete burning out, it is usually a persistent, chronic level of stress that contributes to burnout.
Athlete Burnout
What Is Athlete Burnout?
Burnout is the physical and emotional exhaustion from constant stress.
It is formally defined as a psychological syndrome with three primary symptoms: emotional exhaustion, cynicism, and reduced efficacy.
What Causes Burnout in Athletes?
There are several causes of burnout in athletes, including:
- Lack of downtime outside of sports
- Too competitive a team at a young age
- High expectations from themselves, parents, teammates, and coaches
- Losing enjoyment in the game and still feeling like they need to show up
How Common Is Burnout in Student Athletes?
Burnout is a fairly common occurrence, averaging 10% in all athletes at some point in the season and up to 35% among student athletes.
There are several factors involved in burnout, and more research is needed as it remains challenging to quantify.
How To Prevent Burnout in Athletes?
There are several strategies you can use to reduce burnout, such as:
- Scheduling rest time for yourself
- Looking for ways to promote a better work-life balance
- Adjusting training to reduce overuse injuries
- Openly talking about challenges with peers, your coach, or a mental health professional.
How to Help Athletes with Mental Health
How Do You Improve Mental Health in Athletes?
One strategy for better mental health in athletes is for athletes, coaches, and teams to take mental health as seriously as they do their physical health and training.
Data indicate that the risk of conditions like burnout decreases when success in a sport is defined by meeting intrinsic goals (e.g., what is valuable to the athlete) rather than extrinsically motivated goals and pressure.
What Role Do Coaches Play in Helping Student Athletes With Their Mental Health?
Coaches set the tone for the team and have the ability to create a positive, supportive sporting environment where an emphasis is placed on their athletes’ entire well-being.
Rates of burnout are higher when coaches are more controlling, place an emphasis on perfectionism, and when athletes perceive a negative relationship with their coach.
What Happens When an Athlete Returns to Sports After Taking Time Off for Mental Health?
When an athlete returns to sports after taking time off for mental health, they often experience a mix of relief, renewed strength, and lingering challenges.
Time away can give them the space to rest, recover, and build healthier coping tools, which may improve focus, balance, and performance when they step back onto the field. Still, returning isn’t always easy.
Athletes may feel pressure to perform at their old level, worry about being judged, or fear losing their place on the team.
These concerns are often heightened by the stigma that still surrounds mental health in sports. With strong support from coaches, teammates, and mental health professionals, athletes are more likely to transition back smoothly
How Can Parents Help Student Athletes With Their Mental Health?
Parents can help by modeling healthy coping strategies, supporting their child regardless of their performance, being an ear to listen, and helping their athlete advocate for themselves and their team.
The risk for burnout increases when the adolescent or teen perceives that parents measure their success in a sport based on their performance.
How Can Teammates Support Each Other’s Mental Health in Sports?
Teammates can support each other by listening, encouraging, and normalizing conversations about emotions and mental well-being.
Decreasing conflict within the team and emphasizing effort over performance can promote mental health within a team.
What Mental Health Resources Are Available for Athletes?
There are several mental health resources available for athletes through mental health professionals, such as licensed therapists, medication, or, if in the school setting, school counselors.
Many mental health providers seek additional training and certification in sport psychology and sports medicine. It may be helpful to seek a mental health professional with this type of additional training.
One example is the Certified Mental Performance Consultant® (CMPC). Sports professionals who have completed this program can be found in their online directory.