Serotonin
What is Serotonin?
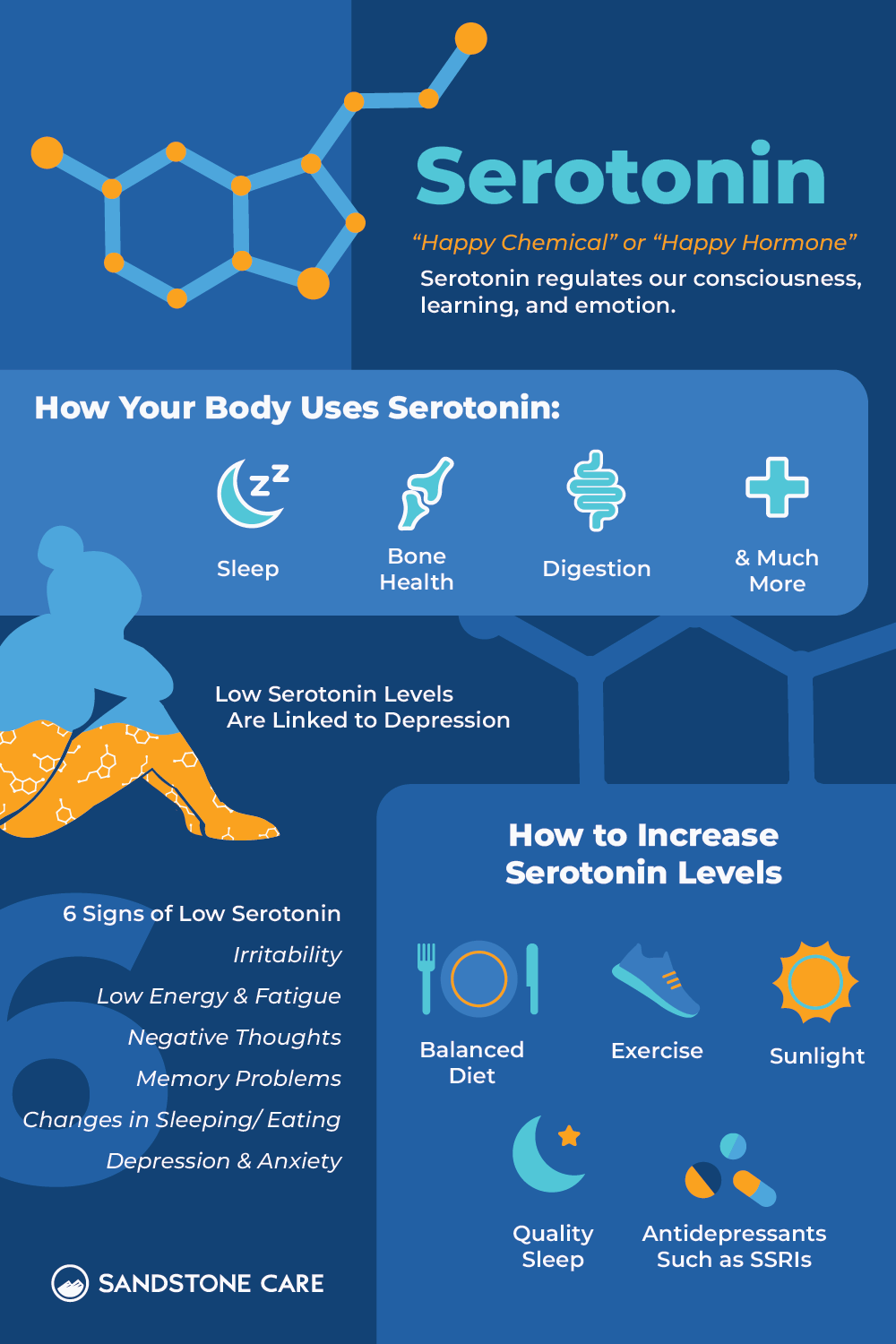
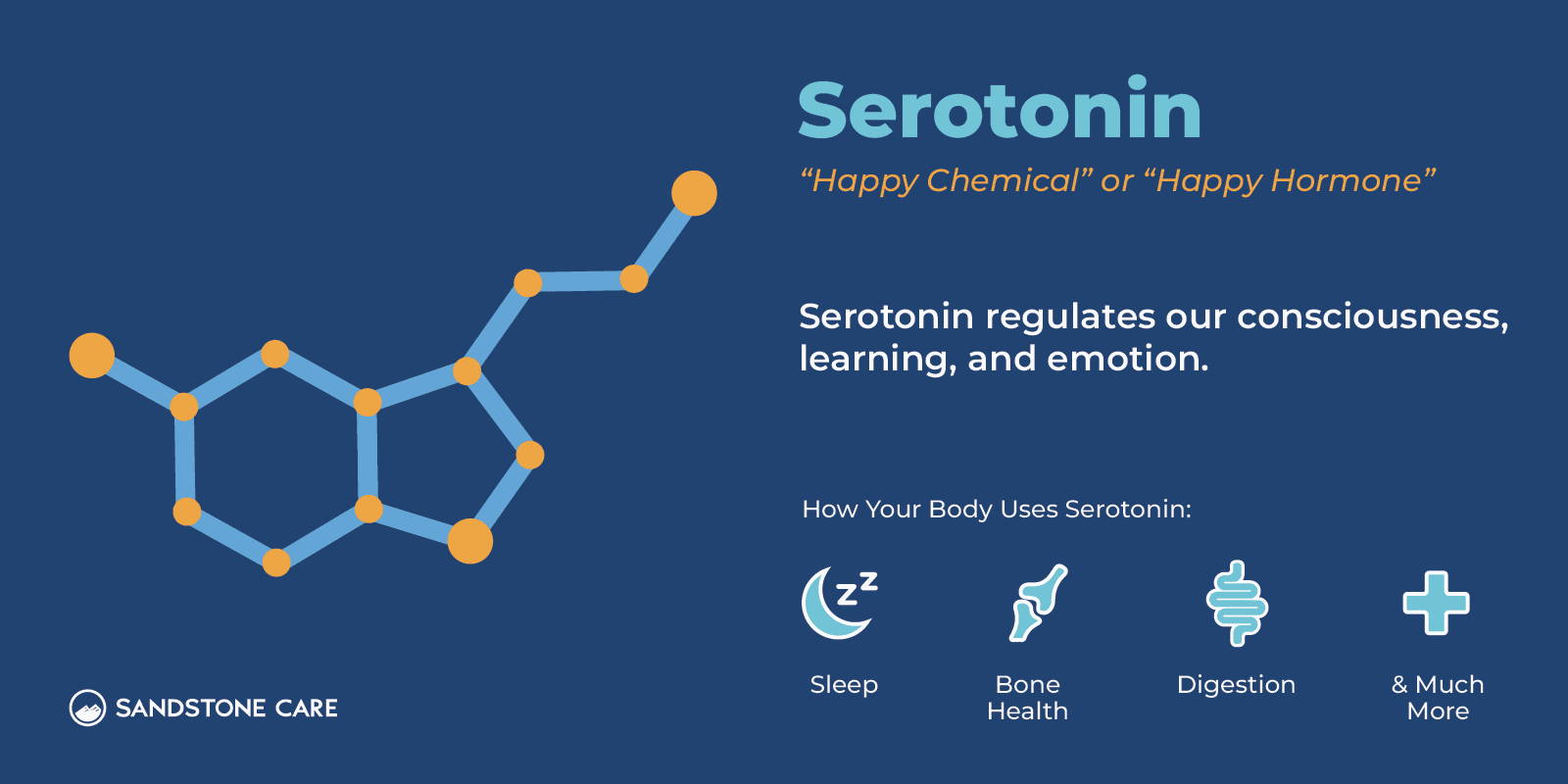
Serotonin is a chemical messenger in the body that helps nerve cells communicate. It affects many important functions, including mood, sleep, digestion, bone strength, sexual function, and even blood clotting.
Most of the body’s serotonin is found in the gut, where it helps control digestion. The rest is made in the brain to support mood and other mental processes.
Because it plays such a big role in feeling good, serotonin is often called the “happy” chemical or “happy hormone.”
When serotonin levels are balanced, it helps keep mood steady, supports healthy sleep, manages appetite, and keeps the body’s systems working smoothly. When levels are too low or too high, it can cause problems like irritability, anxiety, depression, poor sleep, or changes in appetite.
Many people try to boost serotonin naturally through exercise, healthy eating, getting sunlight, and managing stress, while others may use prescribed medications like SSRIs to help the brain use serotonin more effectively.
Dopamine and Serotonin
What Is the Difference Between Dopamine and Serotonin?
The main difference between dopamine and serotonin is that dopamine drives motivation and reward-seeking, while serotonin is focused on maintaining stable moods, sleep, and other parts of well-being.
Dopamine is most active in reward pathways like the mesolimbic system, where it fuels motivation.
Serotonin, which originates mainly from the raphe nuclei in the brainstem, spreads throughout the brain to help regulate mood, emotional balance, and a sense of satisfaction.
Dopamine is like the spark in an engine; it ignites motivation to pursue rewards. It is also essential for movement control and plays a key role in the learning process.
Too little dopamine can leave a person feeling unmotivated, distracted, or physically slowed, as seen in conditions such as depression, ADHD, and Parkinson’s disease.
Serotonin acts more like the steady fuel that keeps the system running smoothly.
It helps maintain mood balance, emotional stability, and a sense of well-being.
Beyond mood, it regulates sleep cycles, appetite, digestion, and even body temperature.
When serotonin levels are low, a person may feel persistently anxious, irritable, or unable to rest, which is common in depression and certain anxiety disorders.
What is the Dopamine and Serotonin Relationship?
Dopamine and serotonin work together but also balance each other out in the brain. For example, in areas like the striatum, dopamine signals that something is worth chasing, while serotonin can step in to slow that urge if it seems risky or not worth the effort.
In the prefrontal cortex, dopamine helps you act quickly and stay focused, while serotonin encourages you to pause and think things through.
When dopamine is high, serotonin may quiet down so you can act fast and go after rewards.
When serotonin is higher, it can hold back dopamine’s impulses, helping you stay patient and make choices that feel good in the long run. This constant back-and-forth keeps you from acting recklessly but also makes sure you don’t lose the motivation to go after what matters.
Where is Serotonin Produced?
Serotonin is widely known as a brain neurotransmitter, but it is estimated that 90% or more of its production takes place in the GI tract, according to the Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology.
In fact, about 90% of the body’s serotonin is found in the digestive system, where it helps regulate bowel movements and function.
It is involved in controlling appetite, influencing blood clotting by triggering the release of platelets, and maintaining cardiovascular health by affecting the contraction of blood vessels.
What Are the Benefits of Serotonin?
When serotonin levels are balanced, they have a positive impact on a person’s mood and emotions through balanced hormones and regulated sleep.
Beyond emotions, healthy serotonin levels can regulate body temperature and breathing, promote healthy intestine function, promote bone health, and much more.
These physical benefits can also improve mood over time through the mind-body connection.
Low serotonin levels are widely known for their association with depression and low moods.
What Role Does Serotonin Play in the Body?
Serotonin plays a vital role in most major organ systems, including the cardiovascular, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, and central nervous systems.
In the central nervous system, serotonin influences emotions, sleep, appetite, memory, and learning. It is one of the key chemicals targeted by antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which increase its availability in the brain to help alleviate symptoms of depression.
Who Should Not Take Serotonin?
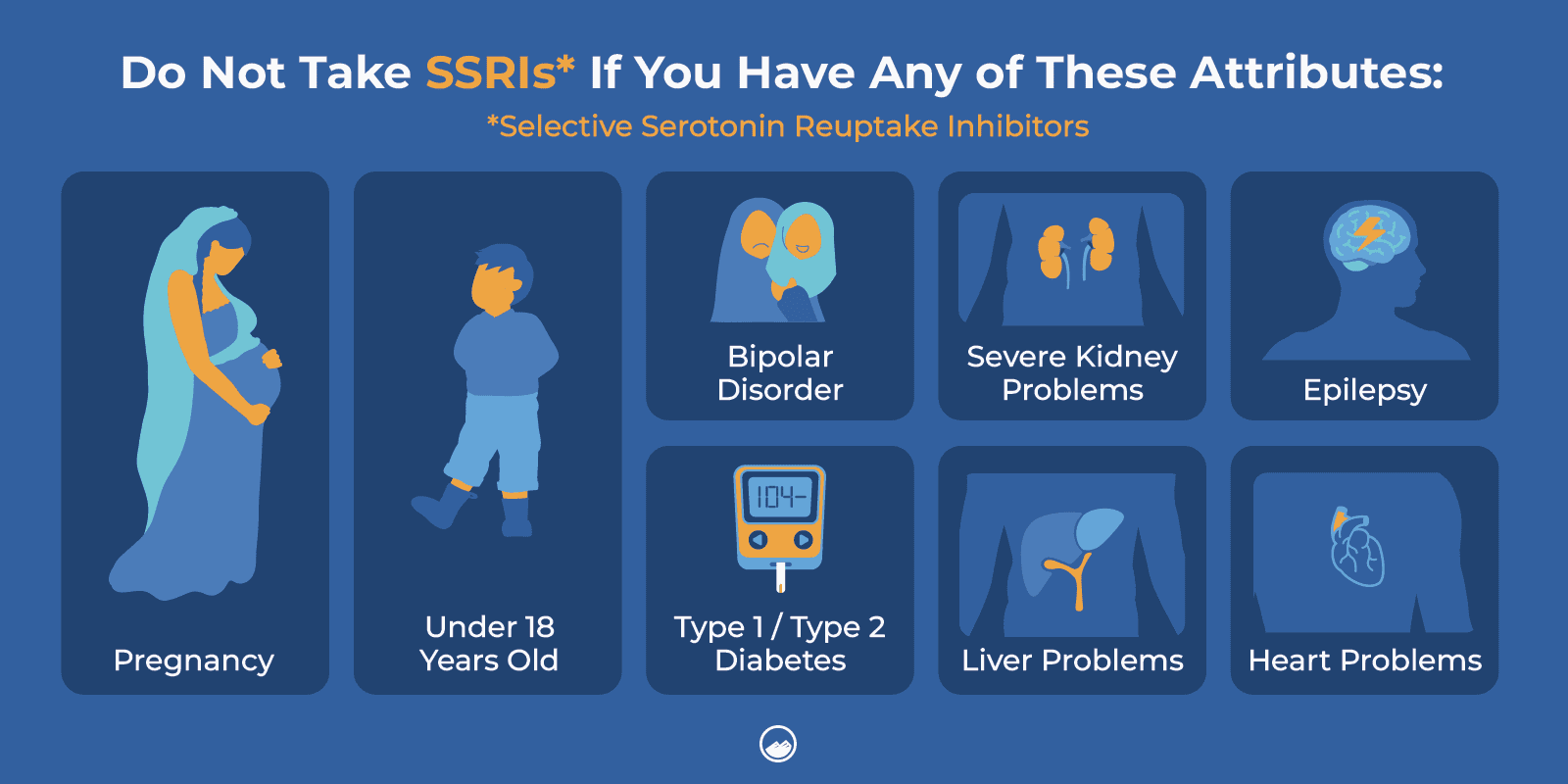
Medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may not be suitable for individuals who:
- Have medical conditions or mood disorders such as bipolar disorder, type 1 or type 2 diabetes, severe kidney, liver, or heart problems, or epilepsy.
- Are pregnant
- Breastfeed
- Are under the age of 18
It is important to consult with your doctor or healthcare provider on whether or not taking a medication with serotonin is safe for you.
While serotonin plays an important role in the brain and body, too much of it can be harmful.
It is also important to let your doctor know of any medications you are taking in case it has an interaction with serotonin medications.
What Produces the Most Serotonin?
It is believed that 95% of the body’s serotonin is produced in the intestines.
Serotonin is produced with the help of an essential amino acid called tryptophan.
When absorbed into the blood, it is carried through the body to help with heart function.
Factors that Influence Serotonin Levels
What Stimulates Serotonin Release?
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is used to make serotonin.
Regular exercise and body movement are the most commonly known way to release tryptophan and boost serotonin.
But, other factors may influence serotonin release, such as exposure to bright light and anti-inflammatory foods.
What Factors Affect Serotonin Levels?
- Genetics
It is believed that some genetic disorders may impact the body’s ability to produce or metabolize serotonin.
- Diet and nutrition
Research suggests that eating tryptophan-rich foods may help boost serotonin levels. Many foods, like foods high in trans fat, do not provide the brain and body with the nutrients it needs and leads to both physical and mental health concerns.Eating other foods, like carbohydrates, may help allow more tryptophan to stay in the blood, impacting serotonin levels.
- Exercise and physical activity
Physical activity and exercise stimulate the release of tryptophan in the body, which helps produce serotonin. It can also help decrease other amino acids, making it easier for tryptophan to reach the brain.At least 30 minutes a day of regular exercise is recommended to help stimulate the release of tryptophan and boost serotonin, resulting in better mood and overall well-being.
- Exposure to sunlight
Exposure to sunlight has been associated with improved moods, specifically in individuals with depression. Studies show that there is a positive correlation between sunlight and serotonin levels, and that they can help with symptoms of depression.For example, for individuals with seasonal affective disorder (SAD), sunlight and vitamin D plays an imperative role in low levels of serotonin, which leads to symptoms such as sad mood and low energy. These effects connect with the seasons and the short, dark days of winter.
- Sleep and circadian rhythm
Studies have also shown that serotonin helps regulate circadian rhythm phases. With this information, there is a possibility that changes in sleep habits can impact serotonin levels.Recent studies have looked into the idea that a night of sleep deprivation may cause an increase in serotonin levels.
Low Serotonin Symptoms
What Causes a Lack of Serotonin?
Multiple factors can lead to a lowered level of serotonin, including:
- Prolonged stress
- Unbalanced diet
- Genetics
- Digestive issues
- Mental health conditions, such as ADHD
- Drugs and alcohol
- Hormone changes
- Lack of sunlight
What Are the Signs of Low Serotonin Levels?
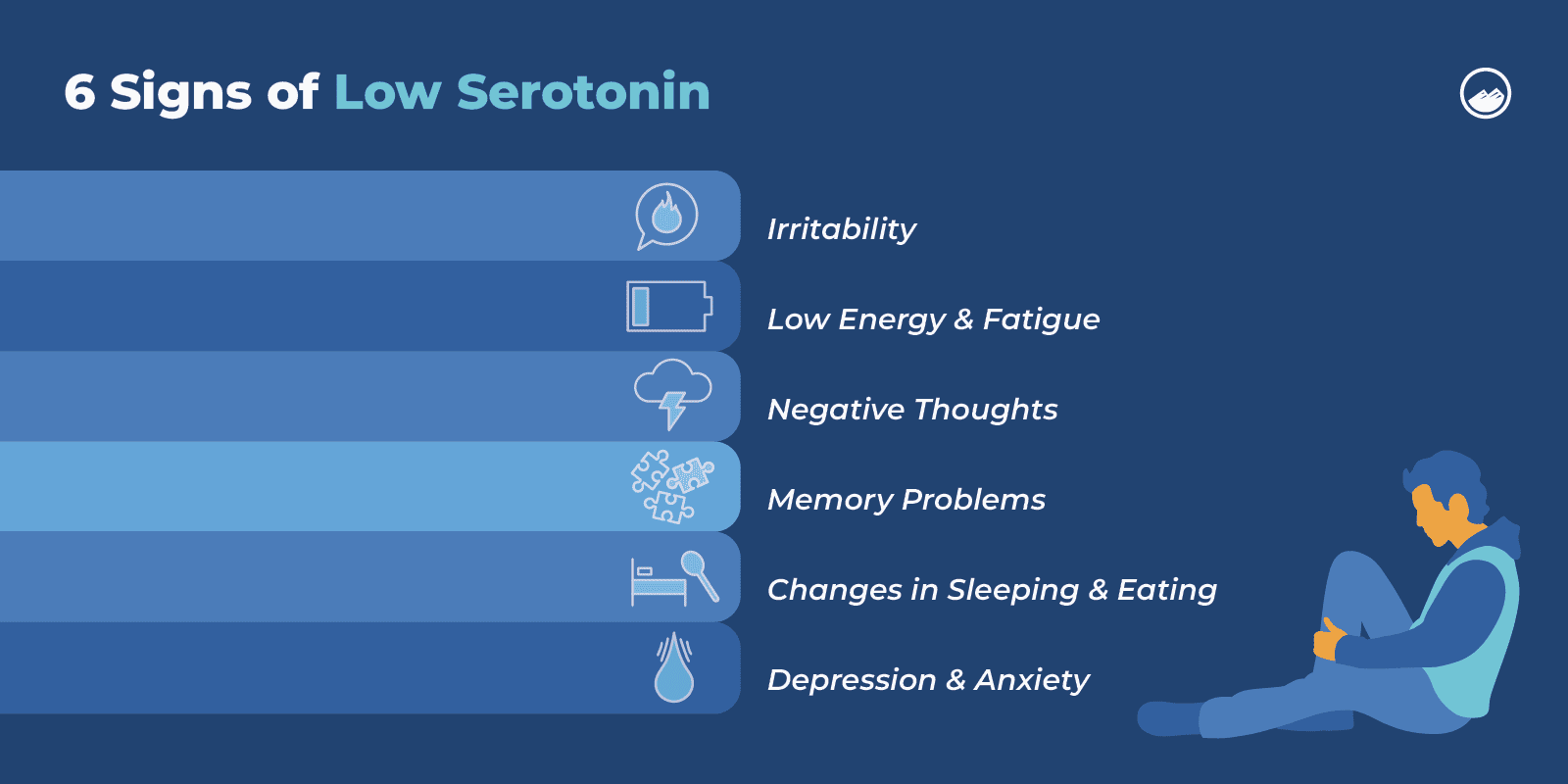
Common signs of low serotonin levels include:
- Irritability
- Low energy and fatigue
- Negative thoughts
- Memory problems
- Changes in sleeping and eating habits
- Depression and anxiety
What Problems Are Associated with Low Serotonin Levels?
Low serotonin levels can be linked to a variety of different physical and mental health conditions, like depression.
Symptoms of serotonin deficiency can also be linked to anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), suicidal thoughts, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
If you or a loved one are experiencing suicidal thoughts, seek help and know you are not alone. Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 988 or call 911.
Other problems associated with low serotonin levels include appetite issues, eating disorders, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and irritable bowel syndrome.
How Can I Check My Serotonin Levels?
A doctor can order blood tests that check serotonin levels in the blood.
If your doctor suspects that the symptoms you are experiencing are related to your serotonin levels, they will do a 5-HT test or a 5-HIAA test.
How Do You Fix Serotonin Deficiency?
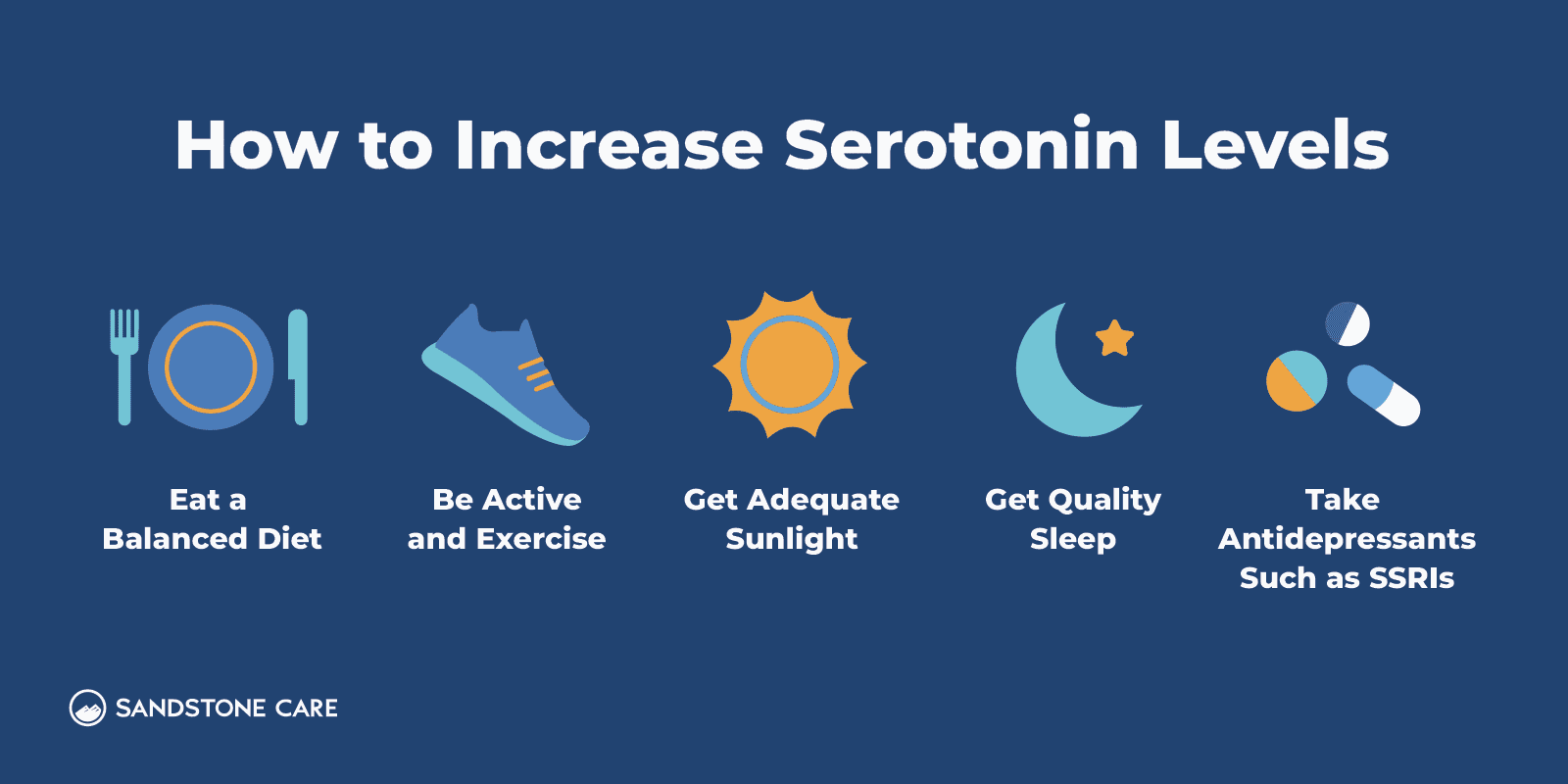
Serotonin deficiency can be improved and managed through natural remedies such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting adequate sunlight.
However, if needed, some medications like antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors can also help individuals with serotonin deficiencies.
How to Increase Serotonin
How Can I Boost My Serotonin?
You can boost serotonin through lifestyle changes (such as exercising more often), medical treatments (such as SSRIs), or a combination of both.
For some people, regular exercise, sunlight exposure, eating tryptophan-rich foods like eggs, nuts, and turkey, getting enough sleep, and practicing stress-reducing activities such as meditation or connecting with others can make a noticeable difference.
These approaches often help with mild mood changes or seasonal dips. If low serotonin is part of a larger issue like depression or anxiety, a doctor may recommend options such as SSRIs, other medications, or therapy to boost serotonin more effectively.
How Can I Increase My Serotonin Levels Naturally?
Sometimes our bodies don’t produce enough serotonin to support our brain and physiological systems. When this happens, there are easy ways we can support our bodies and encourage them to produce an optimal level of the hormone. Natural ways to increase serotonin include:
- Exercise and physical activity
Research shows a clear relationship between exercise and reduced anxiety and depression. Exercise and physical activity can also help increase the amount of tryptophan in the brain, an amino acid that triggers the production of serotonin.
- Exposure to sunlight
Exposure to sunlight and bright light is a standard treatment for individuals with depressive disorders. Many studies show a correlation between exposure to bright light and naturally higher serotonin levels.This could mean spending more time outside in the sunlight and getting more natural light into your home. There are even lamps that are specifically designed to aid in the treatment of seasonal affective disorder.
- Sleep and circadian rhythm
Studies show that sleep deprivation can impact serotonin levels. These studies demonstrate that a night of sleep deprivation can boost serotonin levels.However, it is important to consult with a doctor first if you are planning to try interrupting your sleep, and it is important to have healthy sleep habits and not intentionally deprive yourself of sleep every night to try to boost your serotonin.
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
Meditation and mindfulness practices help increase a person’s awareness and presence at the moment. These practices are associated with improved mood and relief from stress.Some studies show that meditation can not only serve as a treatment for anxiety but also as a preventative medicine, according to Ancient Science Of Life. The idea is that meditation and yoga can influence brain mechanisms that involve gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin, and norepinephrine.
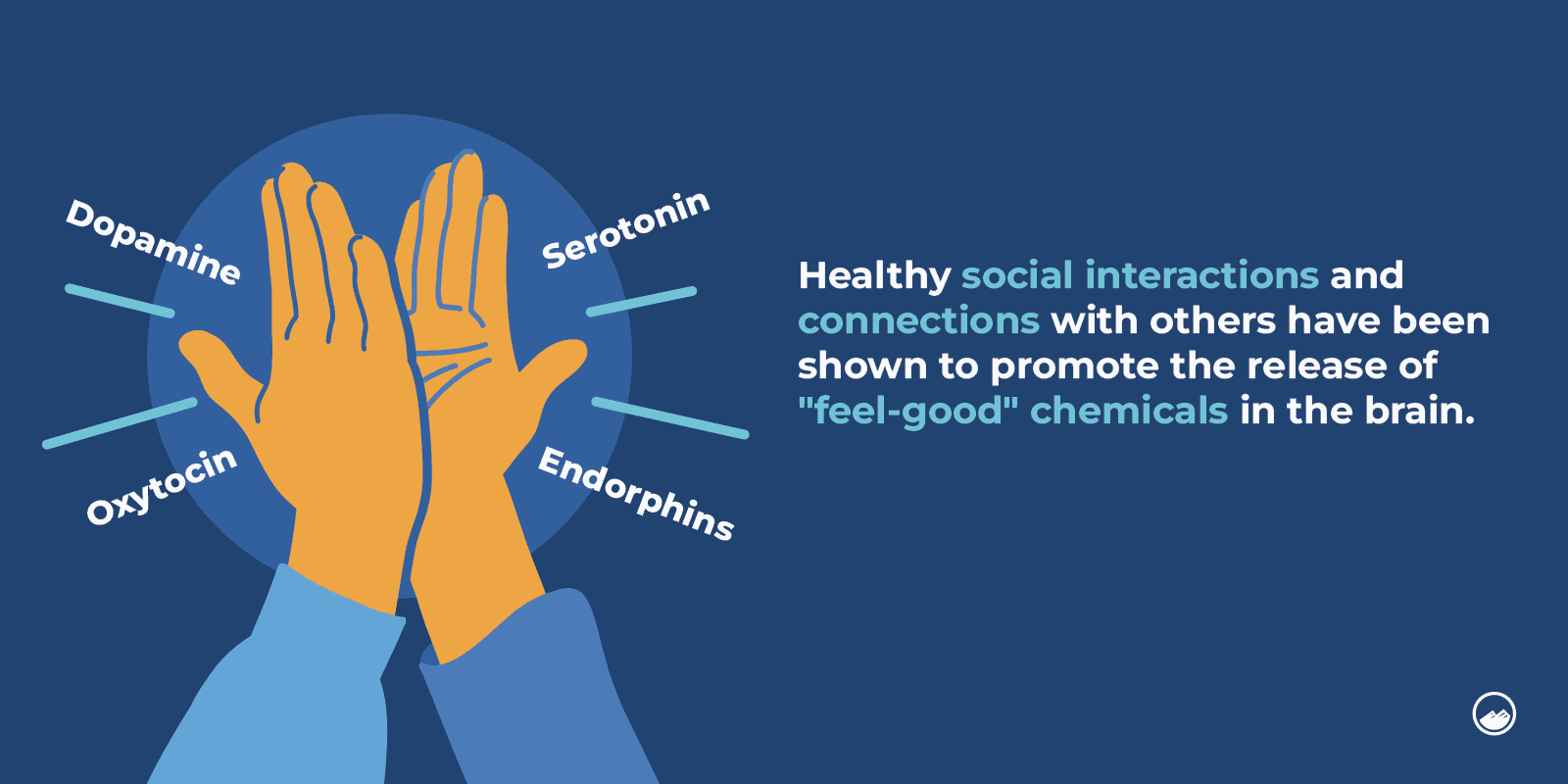
- Social connection and support
Healthy social interactions and connections with others have been shown to promote the release of “feel-good” chemicals in the brain, including dopamine, oxytocin, serotonin, and endorphins.Support plays a big role in a person’s health and overall well-being. When you have people you can go to, it can help relieve stress, improve mood, and promote feelings of comfort and security. - Get a Massage
Massage therapy is incredible for your muscles, but also your mood! Getting a massage is a natural way to increase serotonin and dopamine levels, which leaves you feeling on top of the world. It also decreases levels of cortisol, the stress hormone.There are a number of different massages you can try including deep tissue, Swedish, hot stone, Thai, Shiatsu, acupressure, and aromatherapy. Each has different techniques and benefits to leave you feeling happy and stress-free. - Manage Stress Levels
Experiencing chronic stress can negatively impact your brain’s production of serotonin, leading to feelings of depression and anxiety. Managing stress when it occurs can do wonders for supporting your serotonin levels. Some techniques to manage stress include deep breathing, spending time in nature, taking a bath, Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR), and journaling.Try experimenting with different stress management strategies to see which work best for you.
Foods That Boost Serotonin
What Foods Increase Serotonin?
Changing your diet is another great way to increase serotonin naturally. Try incorporating these natural serotonin boosters into your daily meals:
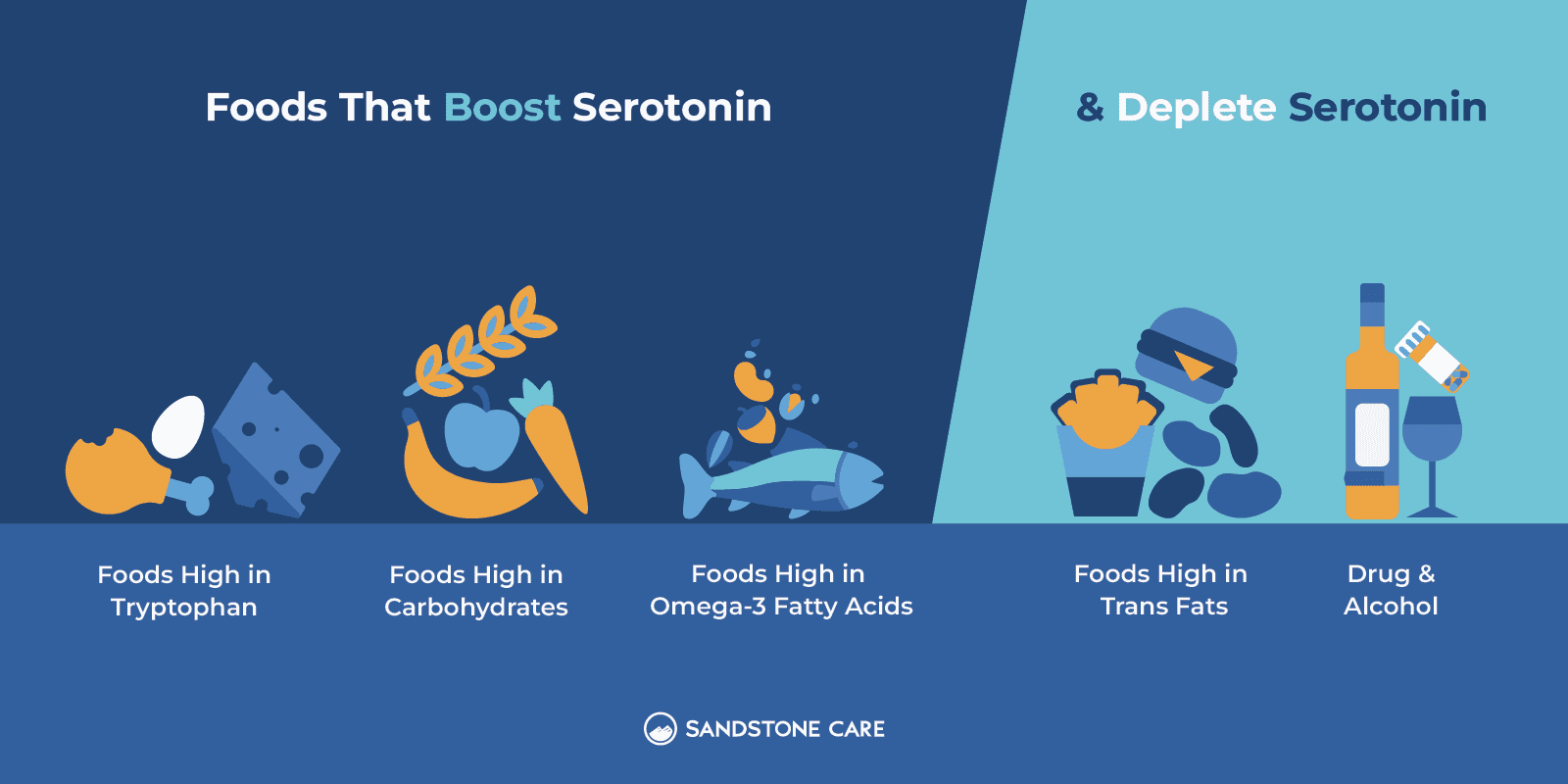
- Foods high in tryptophan (e.g., turkey, eggs, cheese)
Some studies show that foods high in tryptophan can help enhance natural serotonin levels and help improve a person’s mood, emotions, and sleep, such as eggs, turkey, and cheese.
- Foods high in carbohydrates (e.g., whole grains, fruits, vegetables)
Carbohydrates can help the body produce more insulin which plays a role in amino acid absorption and allows for more tryptophan to stay in the blood, which can help boost serotonin levels.Eating carbohydrates along with food high in tryptophan may help boost serotonin levels and maintain them.
- Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., salmon, nuts, seeds)
Omega-3 fatty acids play an important role in regulating the serotonin system. Eating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, nuts, and seeds can help to keep serotonin levels balanced.
What Foods Deplete Serotonin Levels?
Many foods today are high in trans fats, such as potato chips and fast food, which are inflammatory and linked to decreased serotonin levels.
Additionally, alcohol consumption can negatively impact the way the brain produces serotonin and impacts serotonin levels. Abstaining from drug and alcohol use can help a person rebalance their levels.
Which Supplement Can Increase Serotonin?
5-HTP is a dietary supplement that is used to help increase serotonin levels in the brain. However it is important to speak with a doctor to make sure that you are addressing the root cause of your symptoms.
According to MedlinePlus, 5-HTP is possibly effective for depression and may work as well as some antidepressant drugs.
5-HTP does come with some potentially negative side effects, so it is important to consult with your healthcare provider if you plan on taking it to make sure it is safe for you and does not interact with any other medications or supplements you may be taking.
Two other common supplements used for serotonin include St. John’s Wort and omega-3 fatty acids.
Is it Okay to Take Serotonin Supplements?
While many supplements are safe to use, if you are planning on taking serotonin supplements, you should consult with your doctor first.
Some supplements are not regulated, which could put you in danger. Other supplements work for certain people but not for others.
What Herbal Supplements Are Known to Increase Serotonin Levels?
Some of the most common herbal supplements thought to increase serotonin levels may include St. John’s Wort, green tea, turmeric, and ginseng.
However, although they are herbal supplements, it is important to get advice from your doctor or healthcare provider on whether or not these supplements are safe for you.
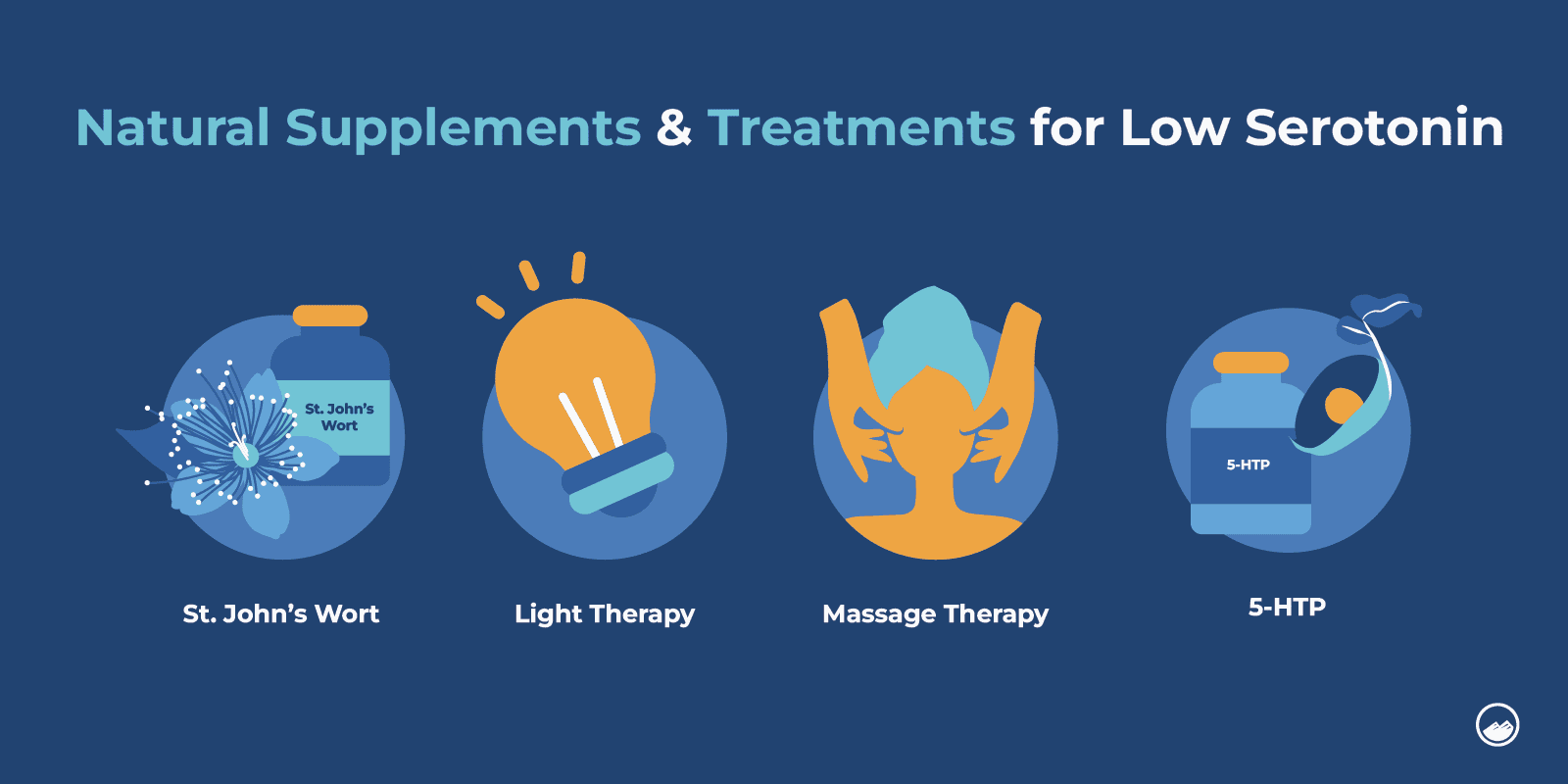
Natural Supplements and Treatments For Increasing Serotonin Levels
- St. John’s Wort
St. John’s Wort is a plant-derived compound that acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and is most commonly a natural alternative remedy for depression or anxiety.
It is important to note that St. John’s Wort is not FDA-approved and is considered a dietary supplement.
- 5-HTP
5-HTP is a chemical byproduct of L-tryptophan and is produced from the seeds of an African plant known as Griffonia simplicifolia.It works by increasing the production of serotonin in the brain and central nervous system.
- Light therapy
According to Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, light treatment can be effective for seasonal affective disorder and also can be beneficial for non-seasonal depression as well.Light boxes are used as a therapeutic approach for certain depressive disorders and deliver a dose of bright light to help treat and manage symptoms of seasonal affective disorder by triggering the release of serotonin.
In these studies, bright light produces greater results than dim light, and morning light produces greater results than evening light.
- Massage therapy
Massage therapy can provide benefits for an individual’s physical and mental health.It can help relieve stress, manage anxiety, reduce irritability, and increase the production of dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin.The stimulation of blood flow through massage therapy plays a role in releasing endorphins, serotonin, and dopamine and also lowers cortisol levels in the body, according to the International Journal of Neuroscience.