Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a form of psychotherapy that was initially designed to help treat borderline personality disorder (BPD) but is now used for a variety of other mental health and substance use disorders.
DBT came about from psychologist Marsha Linehan’s efforts to find treatment for suicidal women.
Through the research of various psychosocial treatments for other mental health disorders, Linehan found that the focus on cognitive and behavioral changes in other forms of treatment led many patients to feel invalidated or misunderstood.
Because of this, she instead focused her DBT treatment intervention on acceptance of yourself, your emotions, your thoughts, and the world.
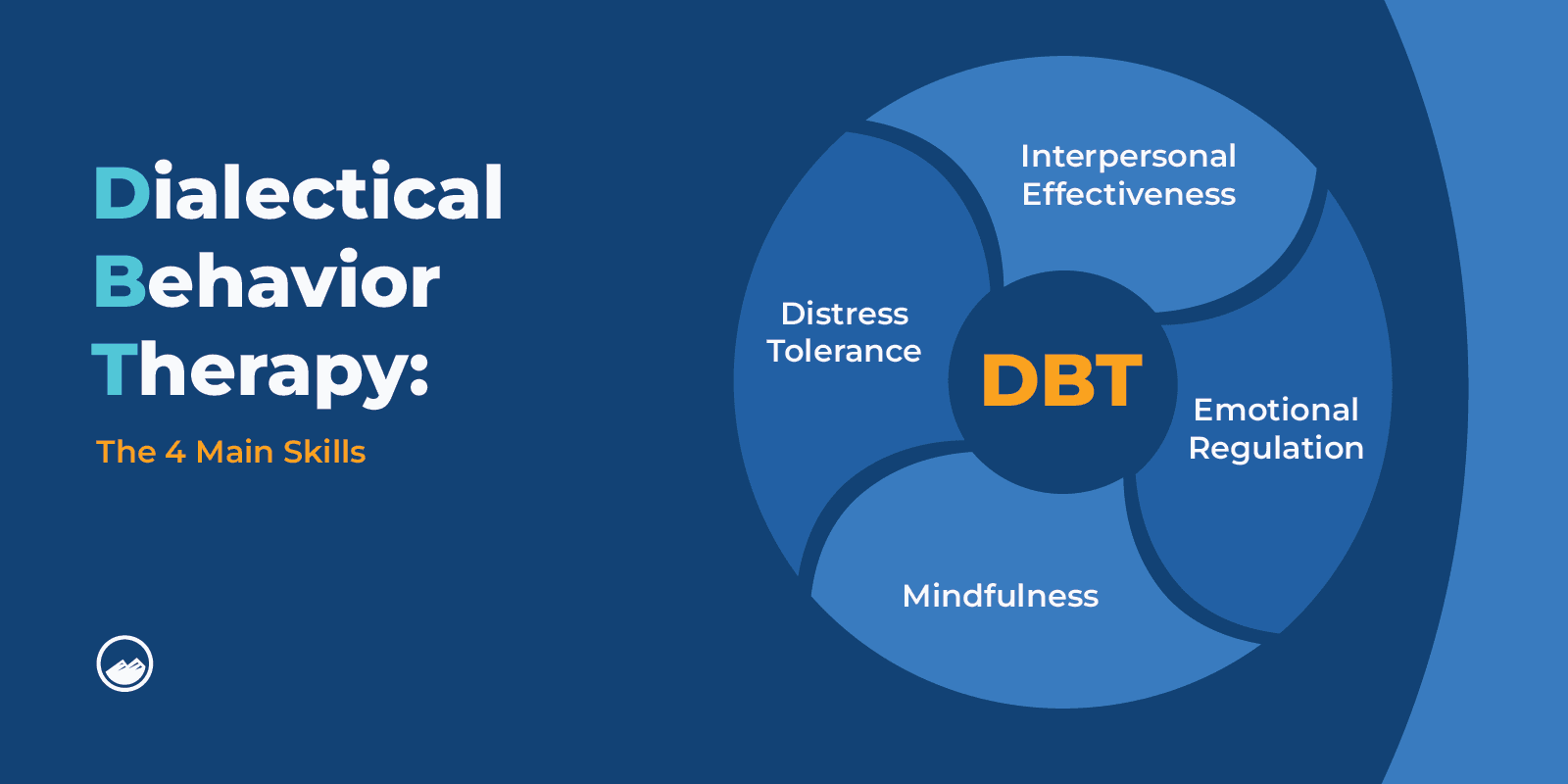
The four main skills of DBT include:
Research suggests that DBT can change the brain and the way people think.
It is considered one of the most effective treatments for borderline personality disorder because of its effect on the brain and mind.
There are some DBT skills that you can work on yourself or can do outside of therapy.
But, if you are just starting, it is generally considered to be most effective with the help of a therapist.
Like any other treatment approach, DBT does not work the same for everyone.
It is also not recommended for individuals with intellectual disabilities or psychotic disorders.

DBT skills training is commonly done in a group setting, which helps teach individuals behavioral skills and how to implement them in their everyday lives.
The 4 skills that are focused on are mindfulness, emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness.
The frequency and length of time DBT is done are dependent on each individual and their unique needs.
There is a certain level of commitment when it comes to DBT, so it is often done in weekly sessions, for about 1 hour each.
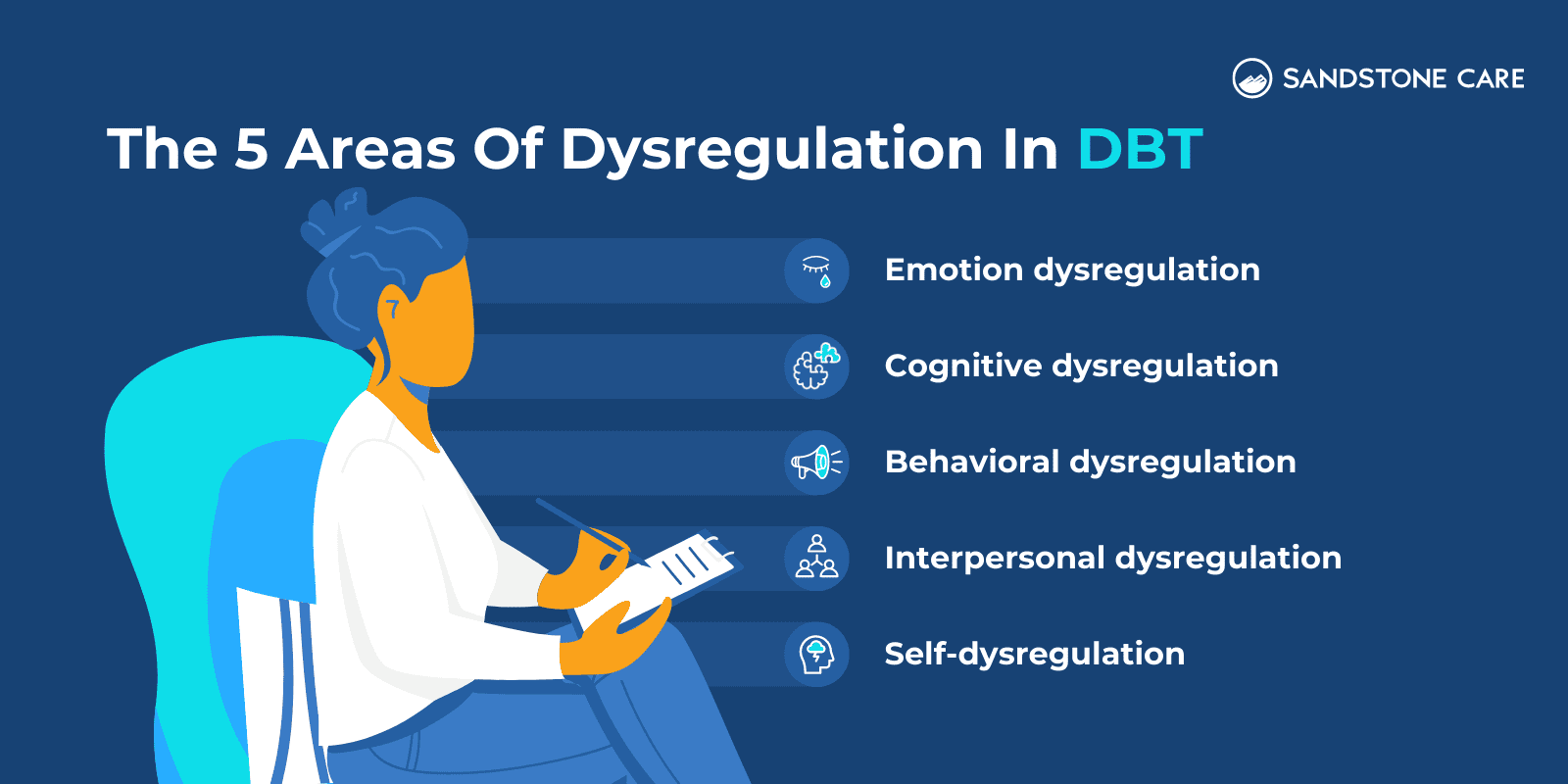
Individuals with BPD commonly exhibit 5 areas of dysregulation that DBT addresses, which include:
The four strategies used in DBT are centered around acceptance and change.
Acceptance-focused strategies include mindfulness and distress tolerance, while change-focused strategies involve emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness.
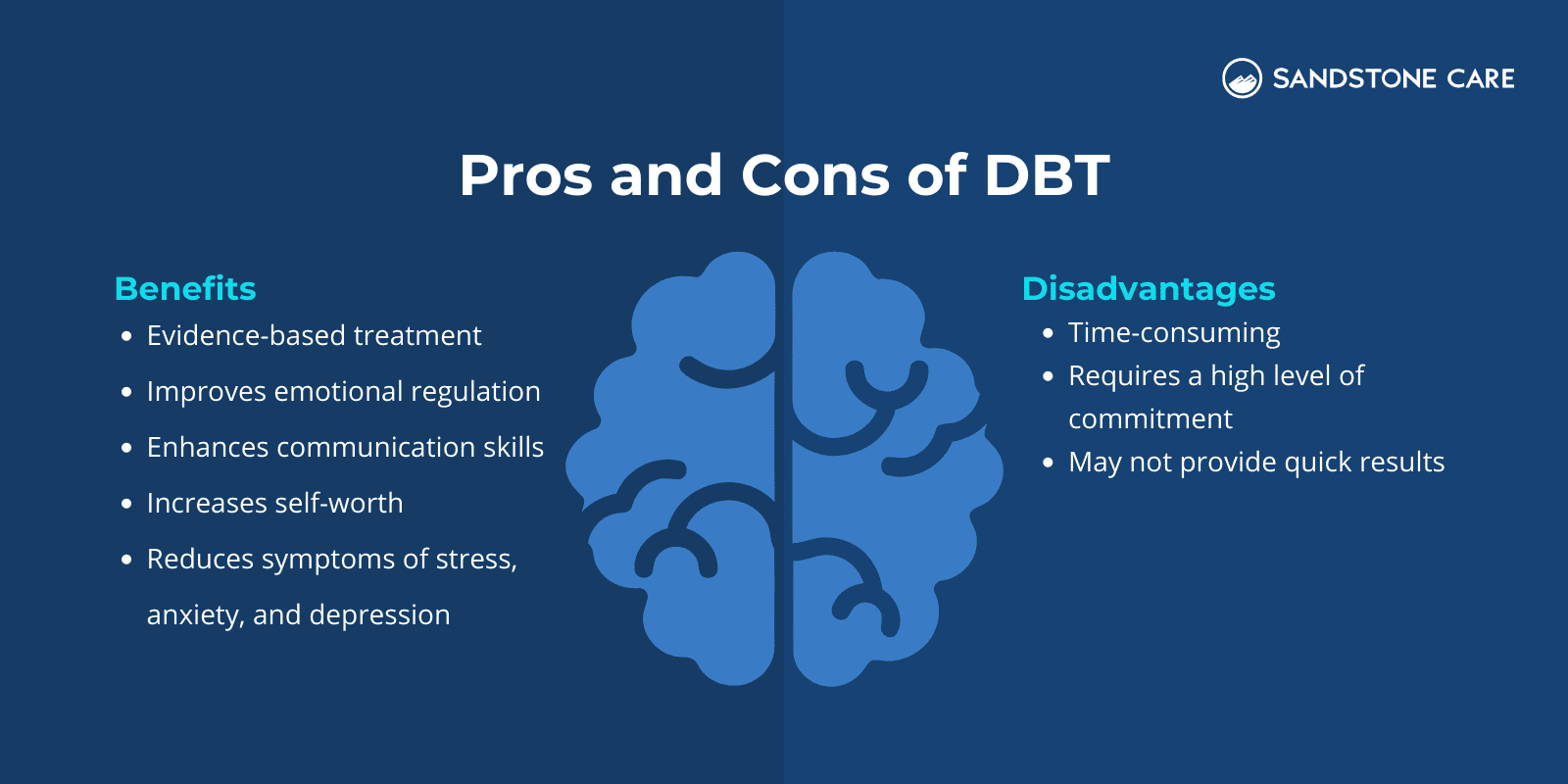
When considering DBT therapy, it is important to address the pros and cons, ask questions, and discuss it with your healthcare provider or a mental health professional.
One disadvantage of DBT is that it can take some time. For someone looking for a quick change, DBT may be frustrating, or it may seem that it is not working.
Along with the length of DBT is the level of commitment. The outcome of treatment is impacted by how committed a person is and how willing they are when they step into therapy.
DBT is an evidence-based treatment approach that can improve the health and well-being of many individuals.
It can help a person learn how to manage and regulate their emotions, improve their communication skills with others, increase self-worth, and reduce the symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression, among many other benefits.
Some of the most common effective communication skills taught in DBT include:

The two communication styles primarily balanced in DBT include reciprocal communication and irreverent communication.
Reciprocal communication involves the therapist’s attention to the individual they are working with and prioritizing their concerns when treating them.
With reciprocal communication, the therapist not only communicates as a therapist but as their authentic self as well.
Irreverent communication is used to shift emotions, thoughts, or behaviors.
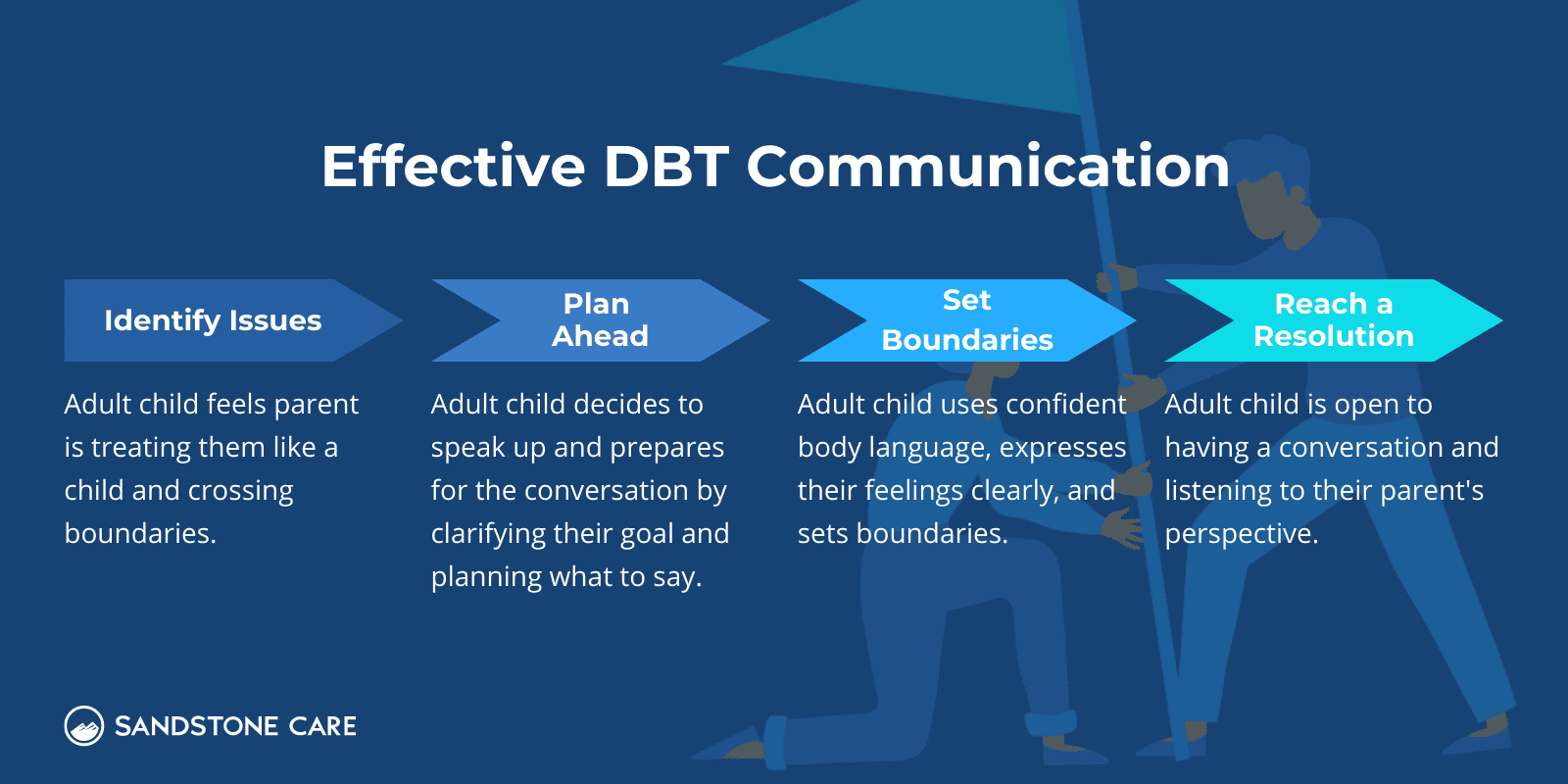
An example of effective communication skills from DBT could be a conversation between a parent and their adult child.
The adult child has been feeling that their parent is treating them like a child and crossing boundaries, so they decide to speak up for themselves.
Their body language shows they are confident, they express how they have been feeling, they are clear about their thoughts and the boundaries that they are setting, and they are open to having a conversation about it and listening to their parent.
The 4 skills taught in DBT are:
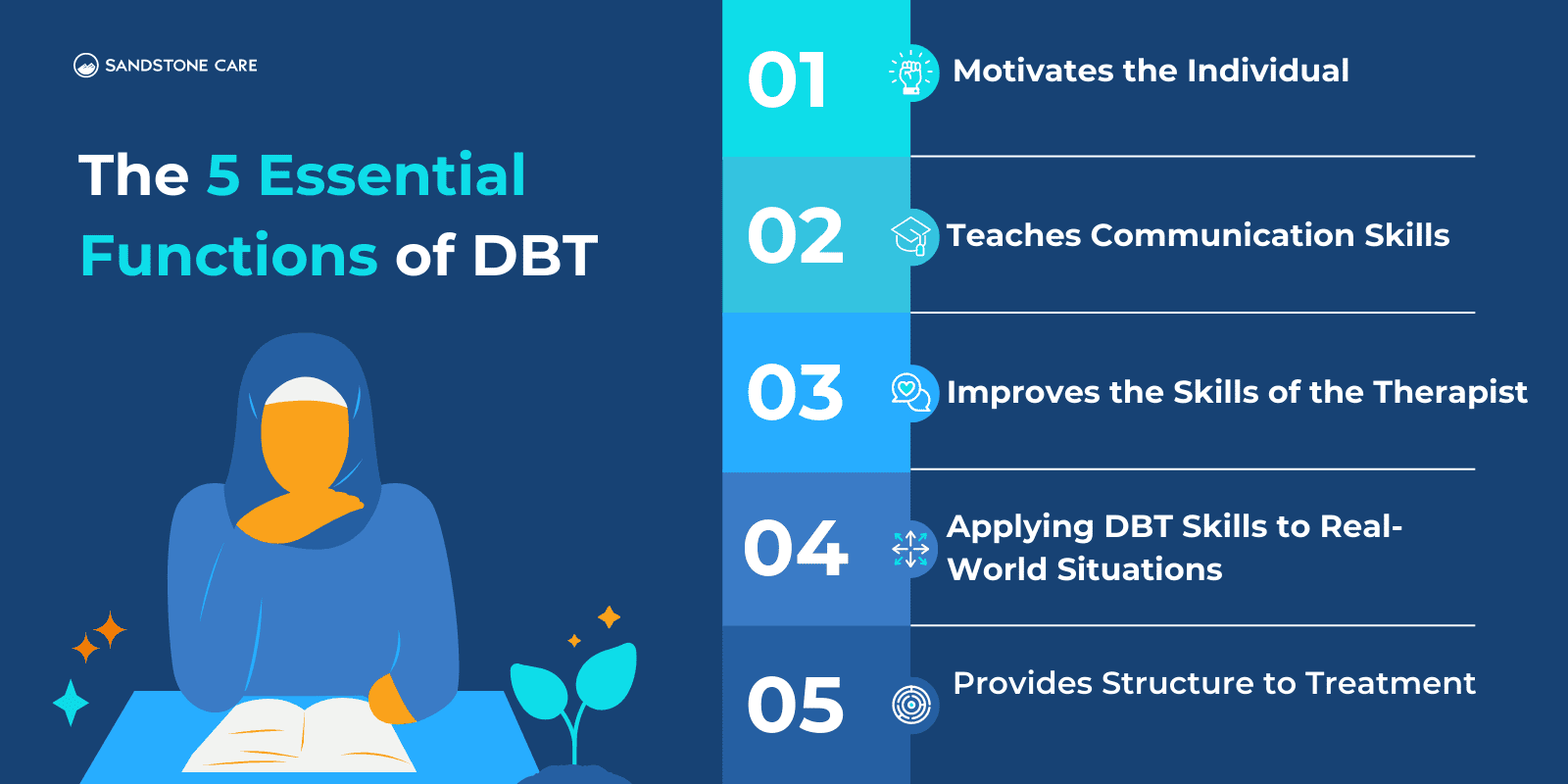
The five essential functions of DBT are:
Learning to self-soothe is considered one of the easiest DBT skills to practice in your everyday life.
Self-soothing involves calming yourself and your emotions through various techniques that are unique to each individual.
Grounding and practicing mindfulness are ways to bring yourself to the present moment and become more aware of your physical surrounding instead of becoming stuck on what is happening internally.
Some people may meditate, others may take a shower or spend time with their pet, but everyone self-soothes in different ways.
Radical acceptance is a DBT skill many people have found impactful and effective.
With radical acceptance, a person can learn how to let go of reality and an attachment to pain. Radical acceptance involves accepting the things that you do not have control over.
Doing this can help a person end a lot of suffering from attachment to pain.
The first DBT skill that should be taught is mindfulness.
Followed by distress tolerance, emotion regulation, then interpersonal effectiveness.
However, these skills may be taught in a different order depending on the therapist and the needs of the individual.
DBT mindfulness skills involve:
When performing these actions, it is also important to do so non-judgmentally, to do one thing at a time, and to do what works best for you.
Mindfulness skills in DBT are broken up into “what” and “how” skills.
There are 6 skills that are focused on when discussing mindfulness in DBT. The “what” skills include observing, describing, and participating at the moment.
Mindfulness is used in DBT as a skill that can help a person find acceptance and learn to manage their emotions to find relief and calmness.
Practicing mindfulness helps bring a person to the present moment and takes attention away from any worries from the past or about the future. It allows you to be aware and practice gratitude as well
The “how” skills are non-judgemental, one-mindfully, and effective.

In DBT, distress tolerance skills focus on developing healthy coping mechanisms to use when faced with difficult feelings or situations.
Common distress tolerance skills in DBT include:

An example of distress tolerance can be seen in a scenario where a person is feeling overwhelmed. Maybe they are having a difficult time at school or work or just argued with their partner.
Instead of automatically responding to the stressful situation impulsively, the person takes a step back to take a mental break. They possibly go outside, go in the bathroom to splash their face with water, or use breathing techniques to calm down and become more present.
With distress tolerance in DBT, the goal is to accept the things you cannot control and focus your attention on the present and the things that are in your control.
DBT can be helpful for individuals living with Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
With PTSD, trauma triggers a person’s distress and can make it very difficult to regulate emotions and cope with difficult memories, feelings, and situations.
When DBT is used to help treat PTSD, techniques like mindfulness, emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness can help a person learn to become more aware of themselves, tolerate and cope with stress, regulate emotions, and build healthy interpersonal relationships.

Common emotion regulation skills used in DBT include:
Emotion regulation skills in DBT can help you gain control over your emotions.
The process of emotion regulation includes:
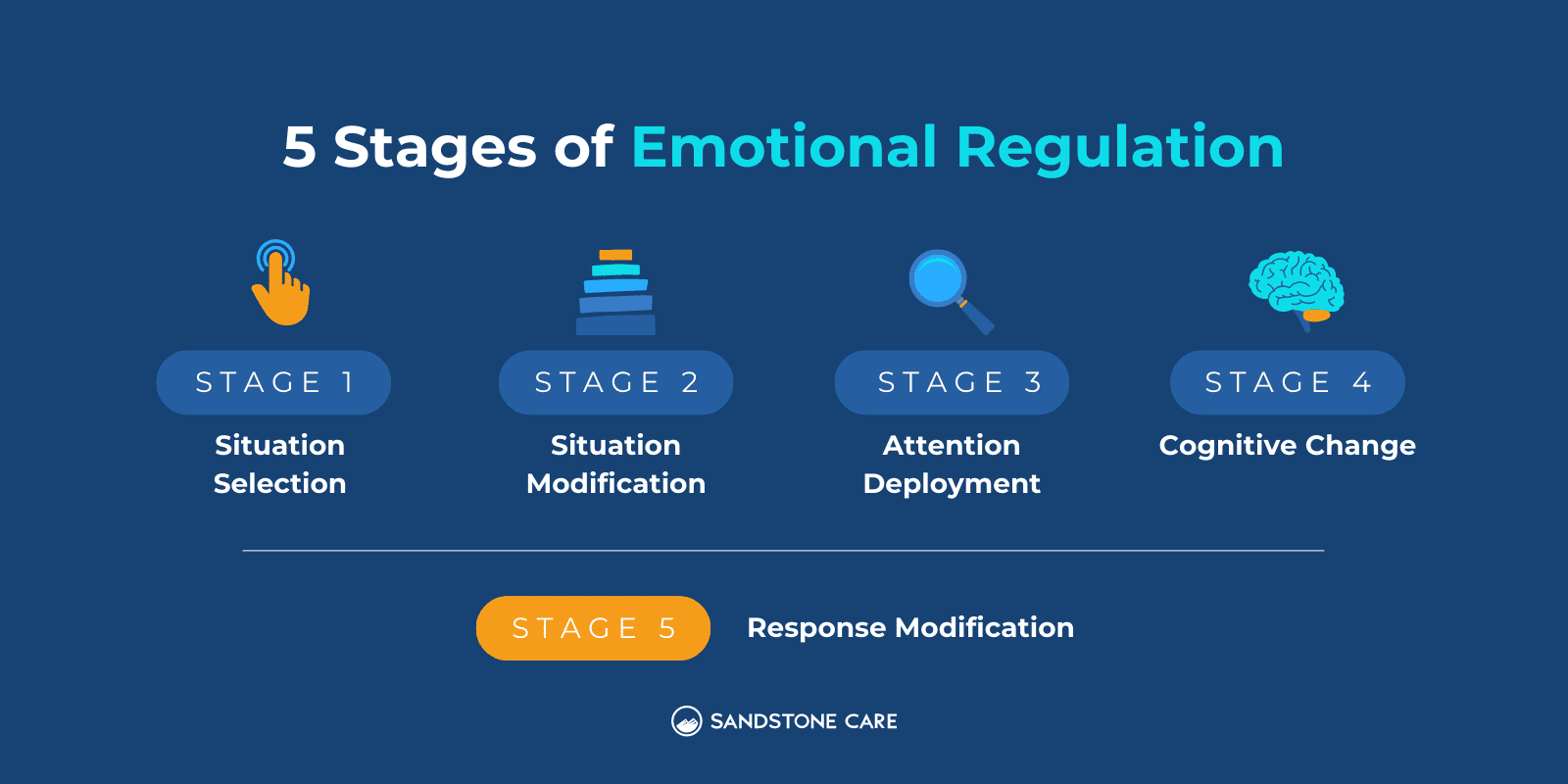
An example of emotion regulation strategies is learning to accept your emotions.
If a person is upset, instead of ignoring it and trying to push it to the side so they can get things done, they begin to accept their emotions and give themselves time to process it.
They may do this by practicing breathing techniques, taking a break outside, or writing out their feelings.
If they would have ignored it, they may build up their emotions that end up resulting in anger or conflict.
Different factors can impact emotion regulation, including:
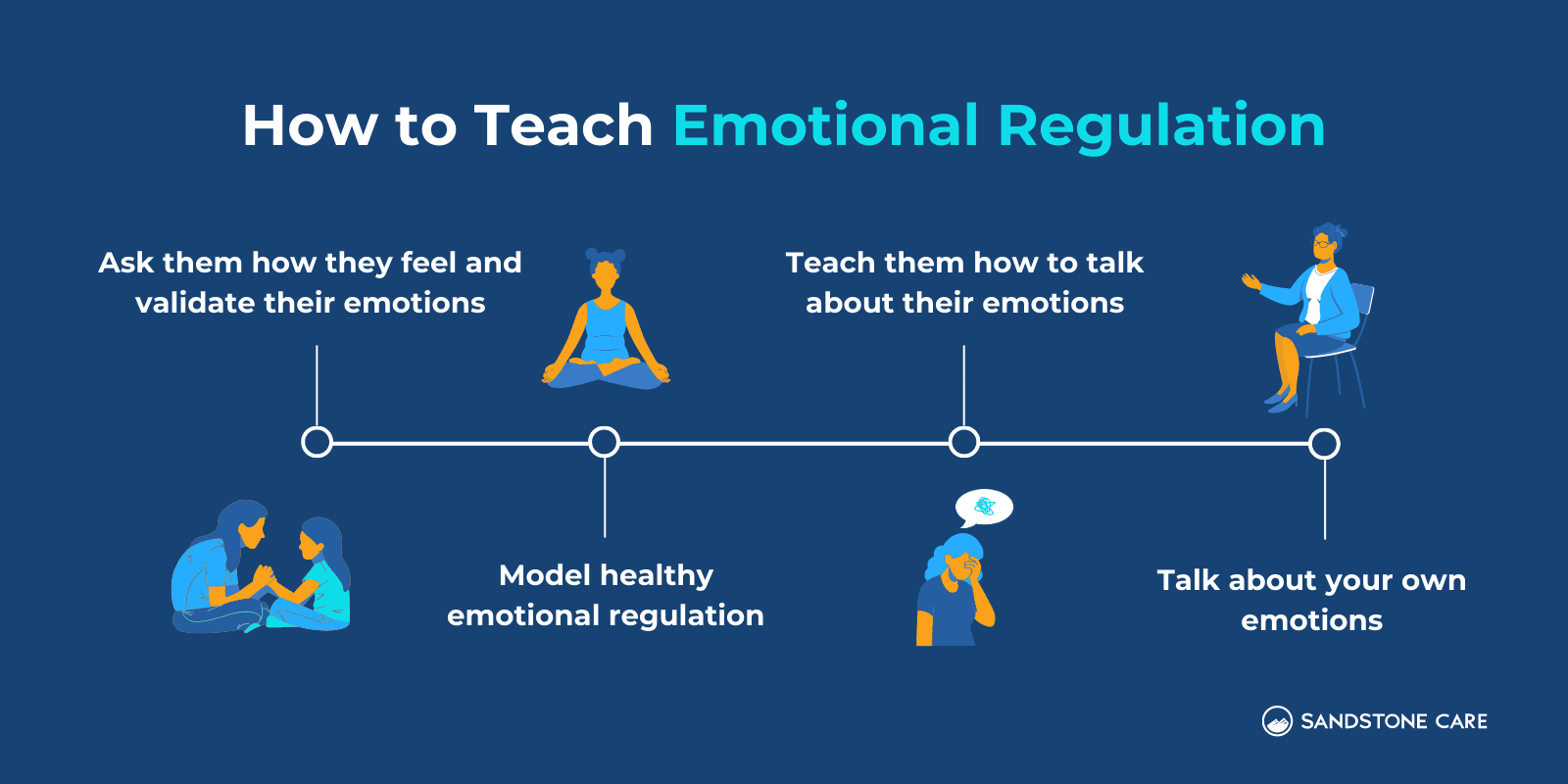
Different ways to help teach emotion regulation to both children and adults are by:
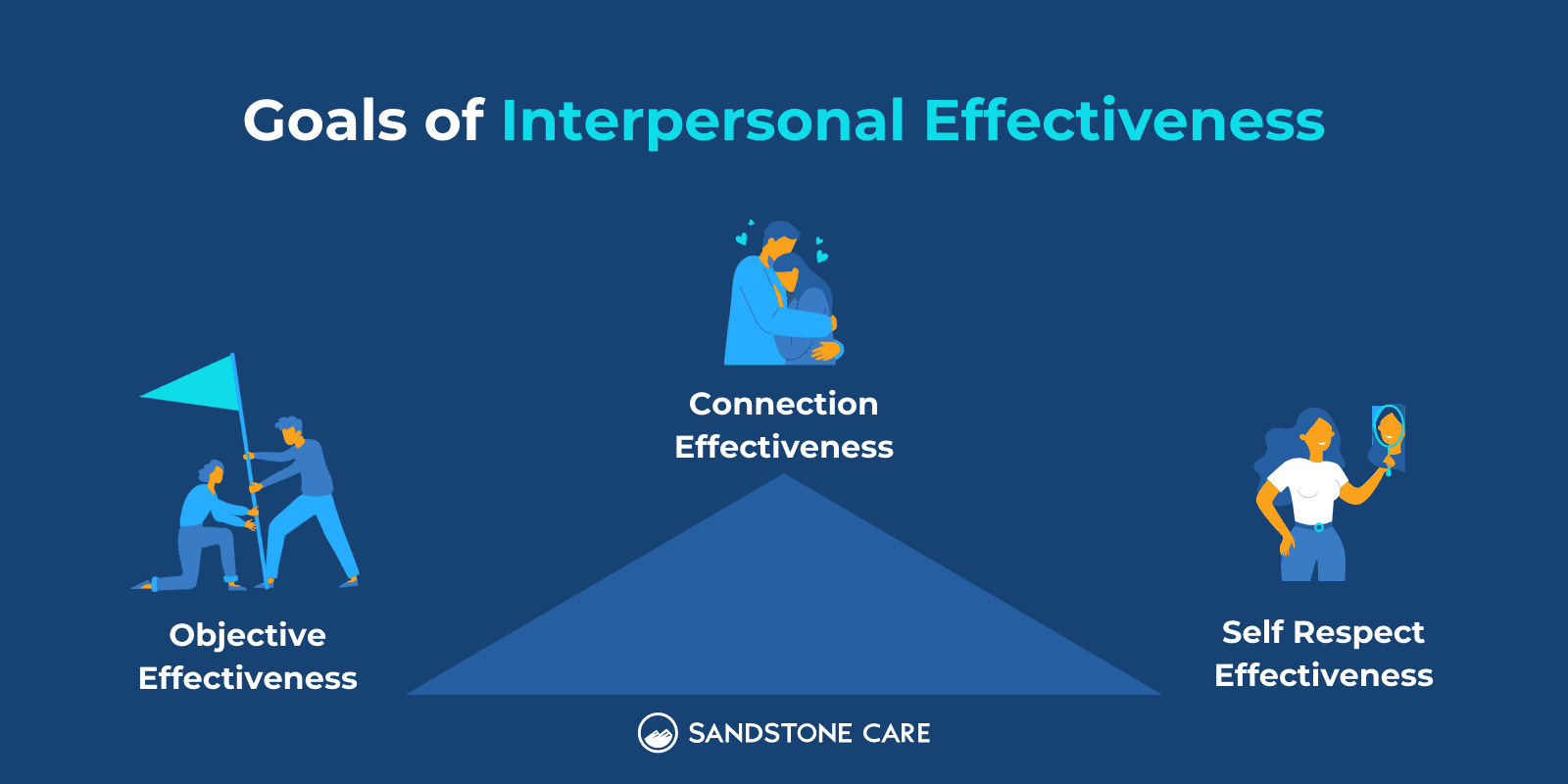
Some of the interpersonal effectiveness skills that are focused on in DBT include:
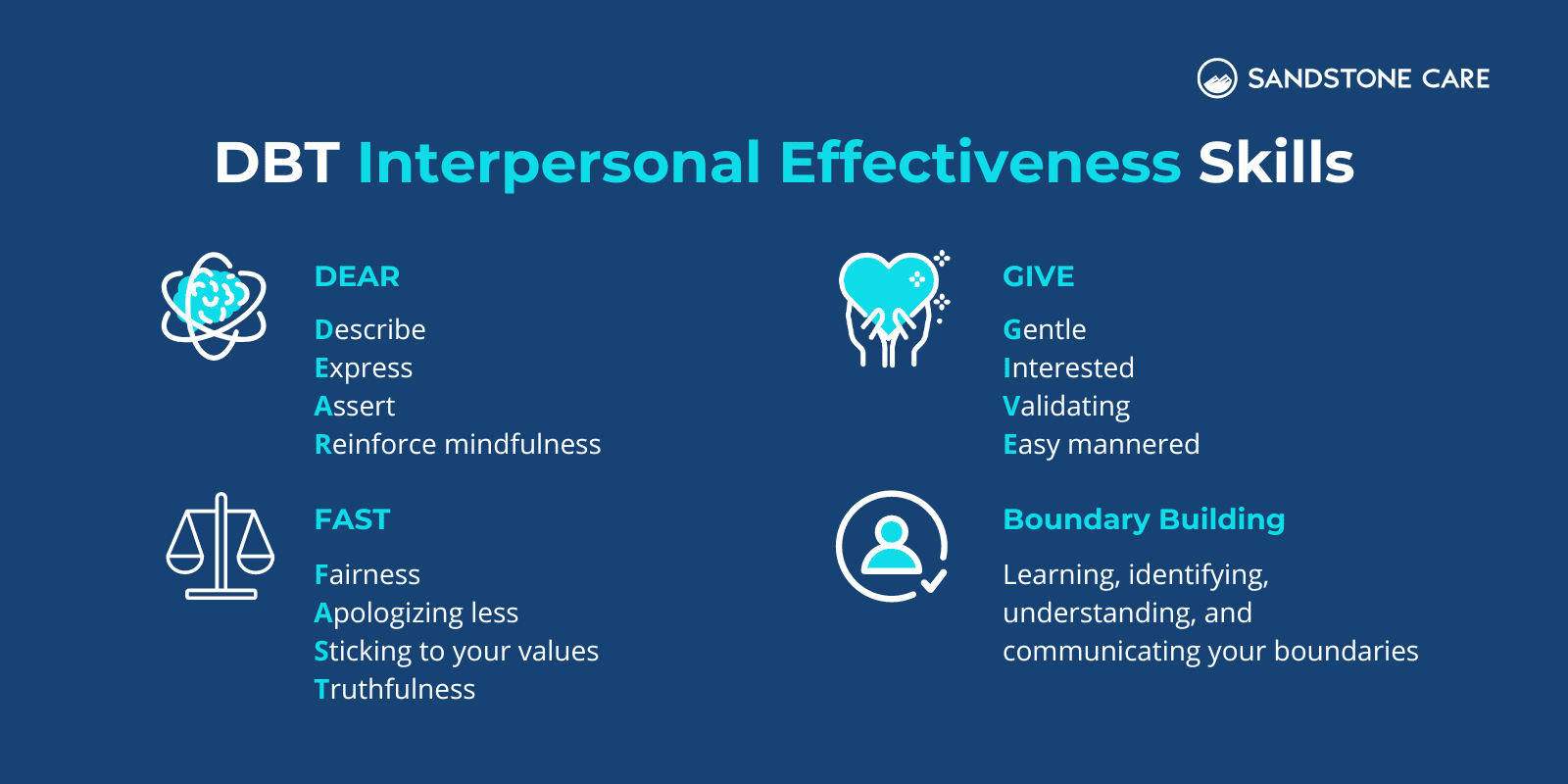
Interpersonal effectiveness skills in DBT help individuals in building self-respect and improving and maintaining healthy relationships.
You can practice interpersonal effectiveness skills by communicating your feelings and desires in a clear and confident way.
Communicating also involves being a good listener and open to hearing another side. But, it is also important to set clear boundaries and stick to your values.
Examples of interpersonal effectiveness skills can include setting boundaries, being able to describe exactly what you need, not being afraid to express your emotions, and validating others’ feelings.
Interpersonal effectiveness skills in DBT have 3 main goals:
The STOP skill in DBT consists of 4 steps:
STOP skills can be used in many different settings.
For example, if a person is faced with a situation that makes them angry, they can physically stop what they are doing and intentionally not act on their urges.
Next, they would take a step back. This can mean they remove themselves from the situation or go outside and talk a walk for a little while.
Then, they observe what is happening around them. Becoming aware of each sense can help bring clarity and calmness to the thoughts and feelings a person has. They might pay attention to the sounds they hear, the smells around them, or their feelings about their surroundings.
Finally, they proceed mindfully. After taking the time to ground themselves and calm down, they move forward and make a decision on how to handle the situation, whether it is talking with the person, taking space from them, or just doing what is best for their mental health conditions.

You can practice STOP skills whenever you are faced with difficult emotions or situations that make you want to act impulsively.
The STOP method is a distress tolerance skill used in DBT.
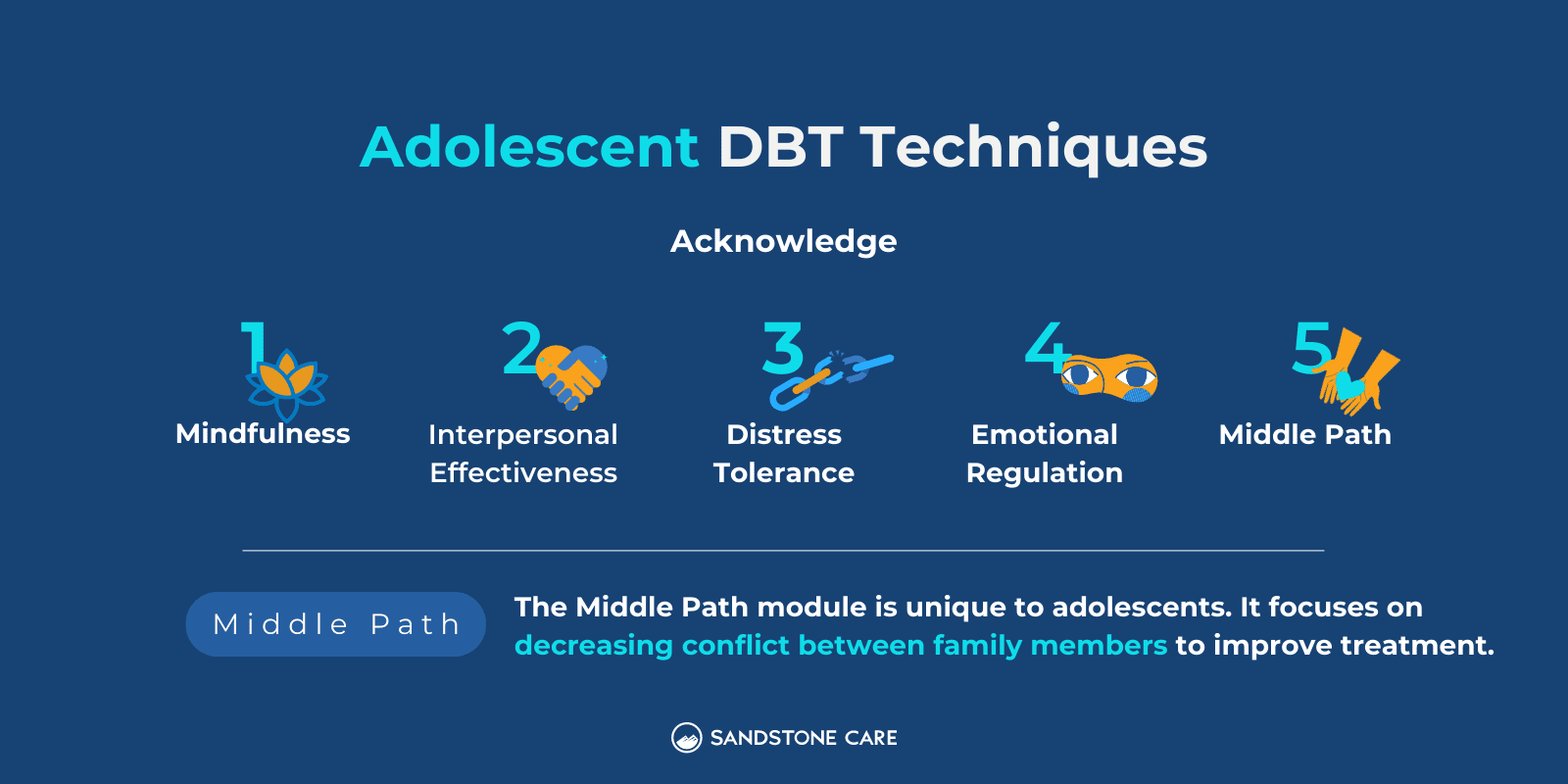
DBT techniques can be helpful for adolescents who may be facing challenges with anxiety, depression, self-harm, and other problems.
When DBT is used for adolescents, caregivers or family members can play an important role in DBT skills training.
Along with the other four DBT skill modules (mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, and emotional regulation), DBT for teens includes an additional module called the middle path.
This skill module can help decrease conflict between family members to help improve the outcome of therapy sessions.
Common DBT distress tolerance skills for children can include:
The STOP skill can help kids manage difficult emotions and situations by stopping, taking a step back, observing, and proceeding with a clear mind.
FAQ
Our goal is to provide the most helpful information. Please reach out to us if you have any additional questions. We are here to help in any way we can.
In DBT, radical acceptance is when one acknowledges the things that are out of their control and stops fighting reality.
Radical acceptance relates to the idea that suffering doesn’t come from pain but rather from holding on to pain.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is similar to mindfulness in how it looks at how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are connected.
However, DBT focuses more on emotion regulation, mindfulness, and learning acceptance.
The 24-hour rule is applicable when a person self-harms or makes a suicide attempt.
If this happens, a DBT therapist will not provide you with phone coaching or calls after you have engaged in self-harming behaviors.
This rule is set in place so that harmful behaviors are not reinforced.
Some of the most popular and highly reviewed DBT worksheets and workbooks include:
DBT workbooks can be very helpful in learning how to implement the skills that you learn in therapy and better understanding the ideas.
Many therapists recommend the use of DBT workbooks outside of individual therapy or group therapy.


Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based therapeutic approach that focuses on acceptance and change. Sandstone Care is here to support teens and young adults with mental health and substance use disorders.