Substance Use Disorder Statistics 2023


Substance use in the United States is evolving rapidly. By identifying and monitoring emerging trends, we can address crises in our communities proactively. Whether you are a medical provider looking to adapt your treatment approach, a journalist looking to provide evidence-based reporting, or a parent learning how to recognize warning signs for your child, it is vital to stay informed. Having the latest and most accurate information empowers us to make decisions that promote the well-being of our families and communities.
By combining the results of Sandstone’s original research with the latest findings from medical associations across the United States, this report provides unique insights into the substance use landscape in 2023.
Substance Use Disorder is defined by the DSM-V as “patterns of symptoms caused by using a substance that an individual continues taking despite its negative effects.” By exploring the usage patterns of substances, we can gain insights into the risk factors that may contribute to Substance Use Disorder in the United States.
Sandstone Care’s 2023 research project was conducted through an online survey that focused on assessing symptoms of mental health and substance use. Questions about substance use concerns centered on subjects like isolation, substance use for coping, loss of interest, and mood changes. Participants had the option to fill out the survey as a self-report, or on behalf of a loved one.*
*Responses were tracked and separated into self-reports and loved-one reports
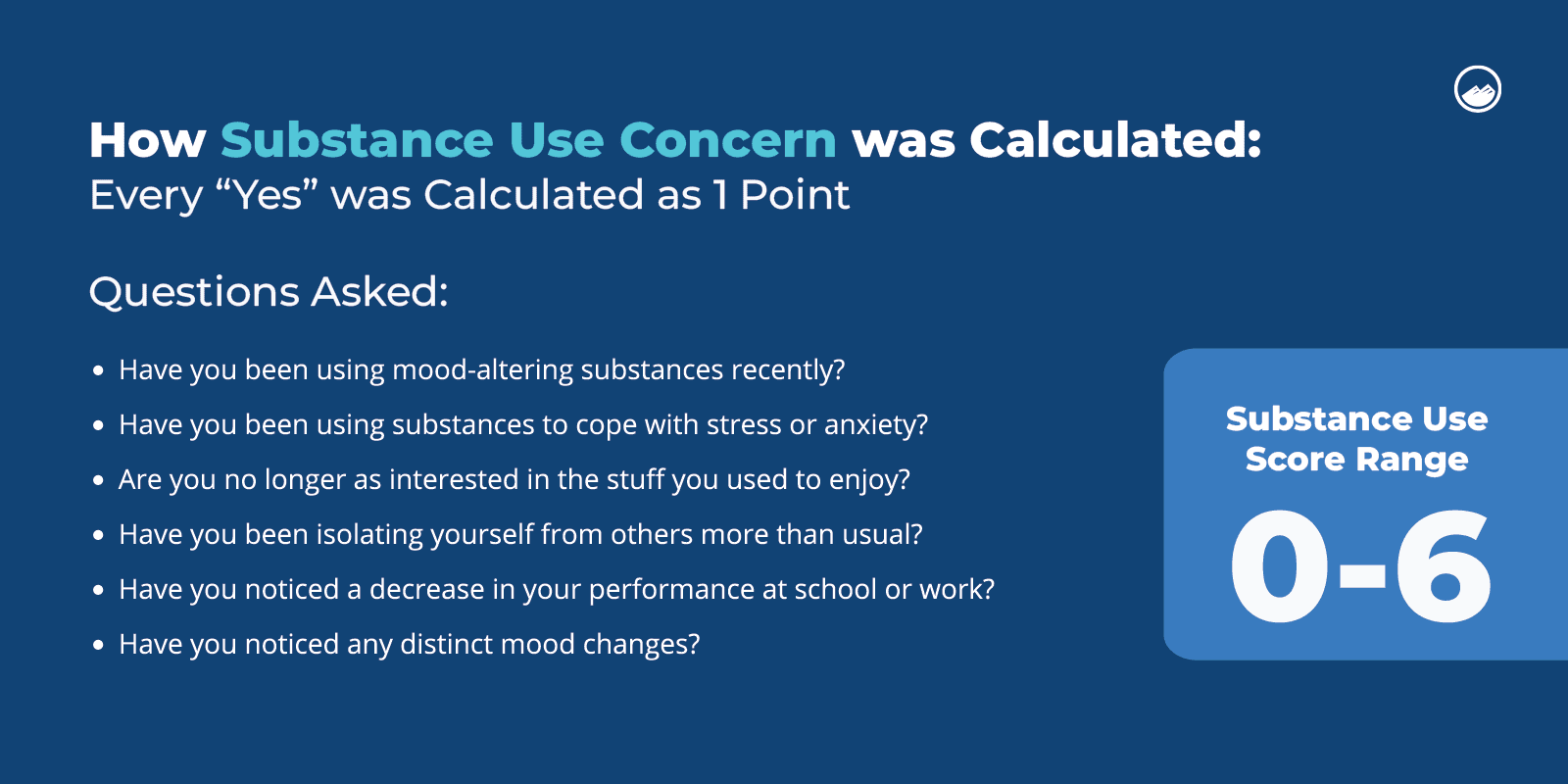
The survey was designed to assess substance use and mental health struggles by using a five-point scale. The scale ranged from least concern (one) to most concern (six).
Sandstone’s clinical team suggests that answering “yes” to 2 or more of the 6 questions below suggests the need for considering treatment options.
Our research focuses on the personal observations of participants, which allows unique insights into the mental health needs of our community. While intake statistics and hospitalizations provide essential information, those numbers are limited to identifying severe cases.
By allowing participants to respond to the substance use, social, and emotional changes that they have observed in themselves or their loved ones, Sandstone’s research can collect results from across the spectrum of substance use experiences.
Teenagers and high school students face unique circumstances that can challenge their well-being and development. Adjusting socially, navigating complex emotions, and feeling misunderstood are common during adolescence. These distinct experiences can drastically impact the relationship between teens and substance use. Young people are particularly susceptible to developing Substance Use Disorder due to a combination of factors. The influence of new social circles and the desire to fit in can drive them to experiment with substances. Teenage brains are still developing, leaving them vulnerable to developing dependencies and addictions that can last well into adulthood.
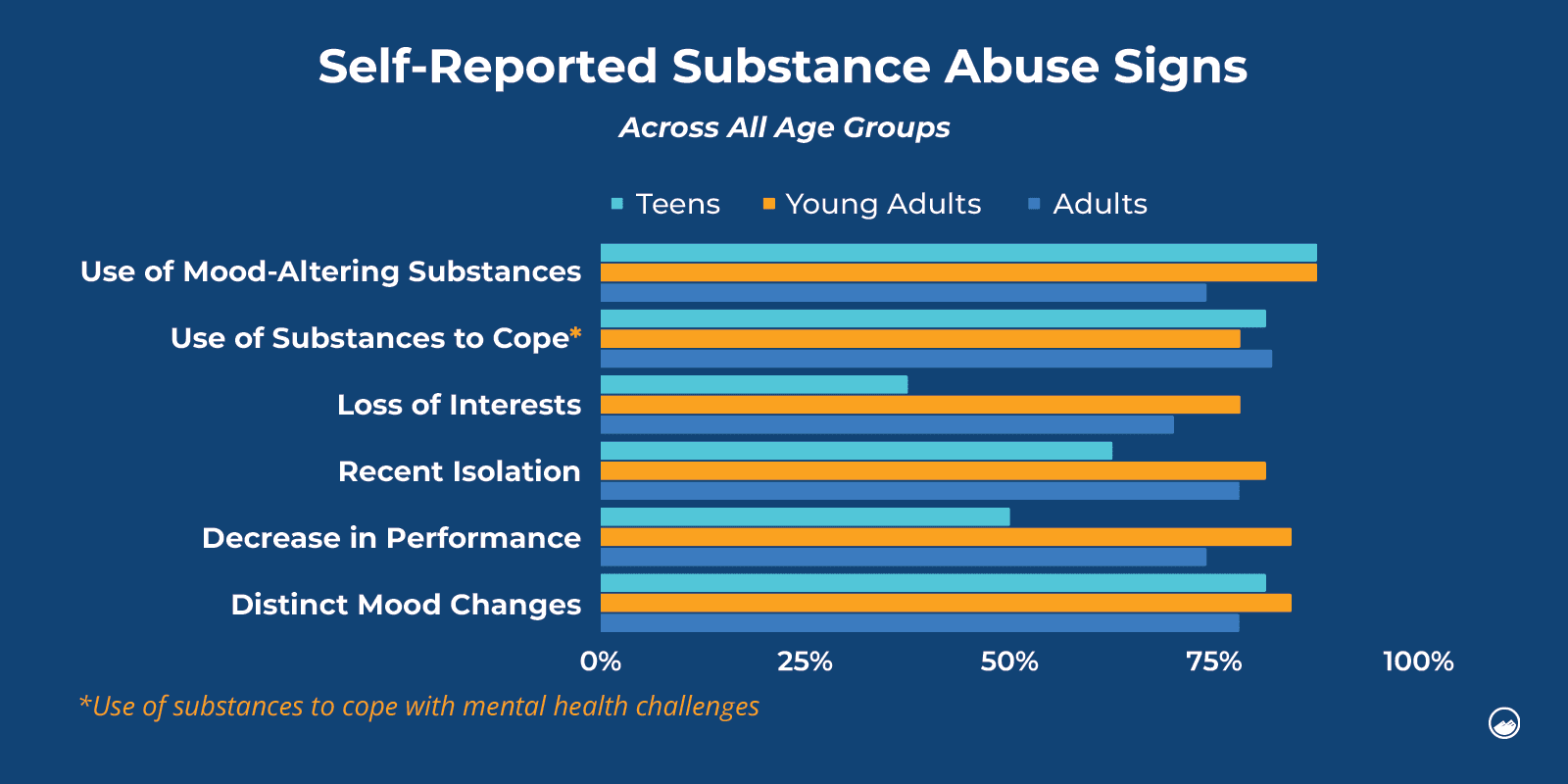
One prominent risk factor observed among adolescents is the experience of isolation and loneliness. Sandstone Care’s findings revealed that feelings of isolation ranked as the second-highest recorded symptom among teen participants. Adolescents who feel disconnected from their peers and support systems are more vulnerable to seeking solace through substance use.
Sandstone Care’s research revealed that out of the teens who reported using altering substances, over 65% of them also reported experiencing all signs of mental health struggles. This highlights the intricate connection between substance use and mental health challenges in teenagers.
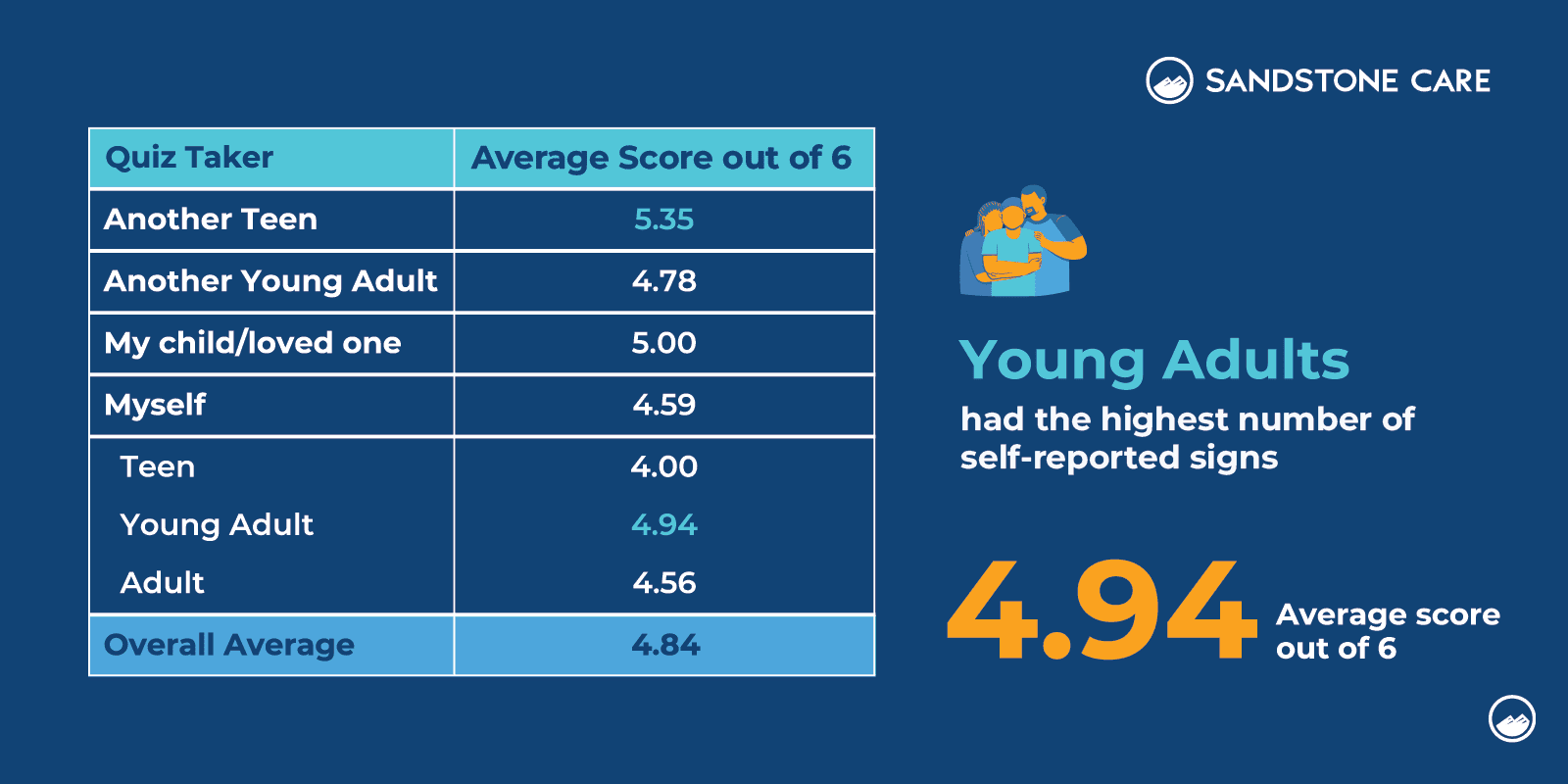
Sandstone Care’s findings indicated that parents, on average, identified the most signs of substance use issues in their teens, with an average score of 5.35 out of 6.
However, it is important to note that while self-reported instances of substance use were lower than other symptoms, factors such as isolation and mood changes were more prevalent across the board. When the test was completed by a concerned loved one, all findings—whether related to substance use or other symptoms—were given equal weight.
This underscores that the perspectives of loved ones can provide valuable insights into an adolescent’s overall well-being.

Studies have shown that the teenage years are a critical period when it comes to substance use. Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that most adults with substance abuse disorders started using during their teenage years. Additionally, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) discovered that about 15% of high school students reported using drugs like cocaine or heroin. Shockingly, the CDC also revealed that 14% of teenagers were misusing prescription opioids, which has been linked to higher rates of risky behaviors, dating violence, and even suicide.
The COVID-19 pandemic had some unexpected effects on substance use among teenagers. According to the NIH, overall substance use rates decreased among middle and high school students during the pandemic. As in-person instruction resumed in 2022, substance use rates remained lower than before the pandemic. However, there was a concerning increase of nearly 300% in opioid use among teenagers, as reported by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
It is crucial to address misconceptions and educate teenagers about the risks associated with substance use. A study by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) found that 57% of high school students do not perceive excessive drinking as harmful.
Young adults are constantly navigating new responsibilities as they enter the workforce and establish their independence. These significant life transitions can bring both excitement and challenges, creating a distinct set of risk factors that contribute to drug addiction among young adults.
Sandstone’s research found that all respondents who expressed concerns about the mental health of another young adult in their life reported that substance use was being used as a coping mechanism. Self-reported responses from young adults demonstrated the highest occurrence of using substances to cope with mental health struggles compared to any other age group.
In assessing signs of substance use issues, young adults identified the most signs of substance use problems when evaluating themselves, with an average score of 4.97 out of 6.
The link between substance abuse and mental health conditions is well-established. Young adults, like individuals of other age groups, face an increased risk of developing substance use disorders when grappling with mental health conditions. The interplay between these factors can create a vicious cycle, where substance use exacerbates mental health struggles and vice versa. Understanding this connection is vital in developing comprehensive treatment approaches that address both substance use and mental health needs concurrently at the same time.
SAMHSA reports that 5.1 million young adults struggle with Substance Use Disorder (SUD), with a majority not seeking treatment. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that young adults had the highest rates of nicotine use, primarily through vaping, which now surpasses traditional cigarette use by threefold.
Illicit drug use was also highest among young adults, aligning with Sandstone’s findings. According to the CDC, young adults faced a high burden of mental health issues, with 11.4% experiencing serious mental illness, and co-occurring conditions of mental health problems and substance use were more prevalent than previously thought.
Binge drinking emerged as the most prevalent substance misuse among young adults, while SAMHSA found that the use of simultaneous alcohol and marijuana (SAM) has increased among college students in the last decade. These insights highlight the pressing need for targeted interventions, expanded treatment access, and tailored prevention strategies to address substance use challenges among young adults.
Adults navigate ongoing social and professional pressures and the responsibility of providing for their families. These stress factors contribute to unique risk factors for drug addiction among adults. Sandstone’s survey found that adults experience high rates of isolation and mood changes as significant symptoms observed in adults.
Among adults, the most commonly reported substances were opioids, cannabis, binge drinking, and prescription drugs. These substances pose substantial risks associated with various health and social consequences. Sandstone’s adult-specific findings revealed that 54% of participants reported substance use challenges. The survey also found 34% of adults experienced all six signs, including substance use, indicating that the majority of those who used substances showed high indications of serious mental illness.
In the realm of adult substance use, the numbers reveal a concerning reality. According to SAMHSA‘s annual report, approximately 17.2% of adults engage in illegal drug or illicit drug use. Additionally, the CDC highlights that a staggering 65.8 million adults admit to consistent binge drinking. SAMHSA found that 5.5% of adults, equating to 14.1 million individuals, experienced serious mental illness in the past year, which is often linked to substance use. The gravity of the situation is further emphasized by the NIH’s discovery that over 70,000 drug overdose deaths occur annually in the United States.
Substance use and substance use disorders (SUDs) have become significant public health issues. SUDs (formerly known as drug use disorder) refer to problematic substance use that can lead to various negative consequences. The link between SUDs and drug overdoses has raised concerns as a public health crisis. Specific SUDs, such as alcohol use disorder (AUD) and opioid use disorder (OUD), have distinct symptoms and impacts on individuals.
Sandstone’s research on substance use revealed common signs among individuals surveyed. These signs included the recent use of mood-altering substances, using substances to cope with stress or anxiety, and experiencing distinct mood changes. Notably, these signs were observed across all age groups, emphasizing the widespread nature of substance use issues.
Understanding the prevalence of these signs and the impact of substance use is crucial for developing targeted interventions and treatments. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to substance use disorders, we can work towards promoting healthier and substance-free lives for individuals of all age demographics.

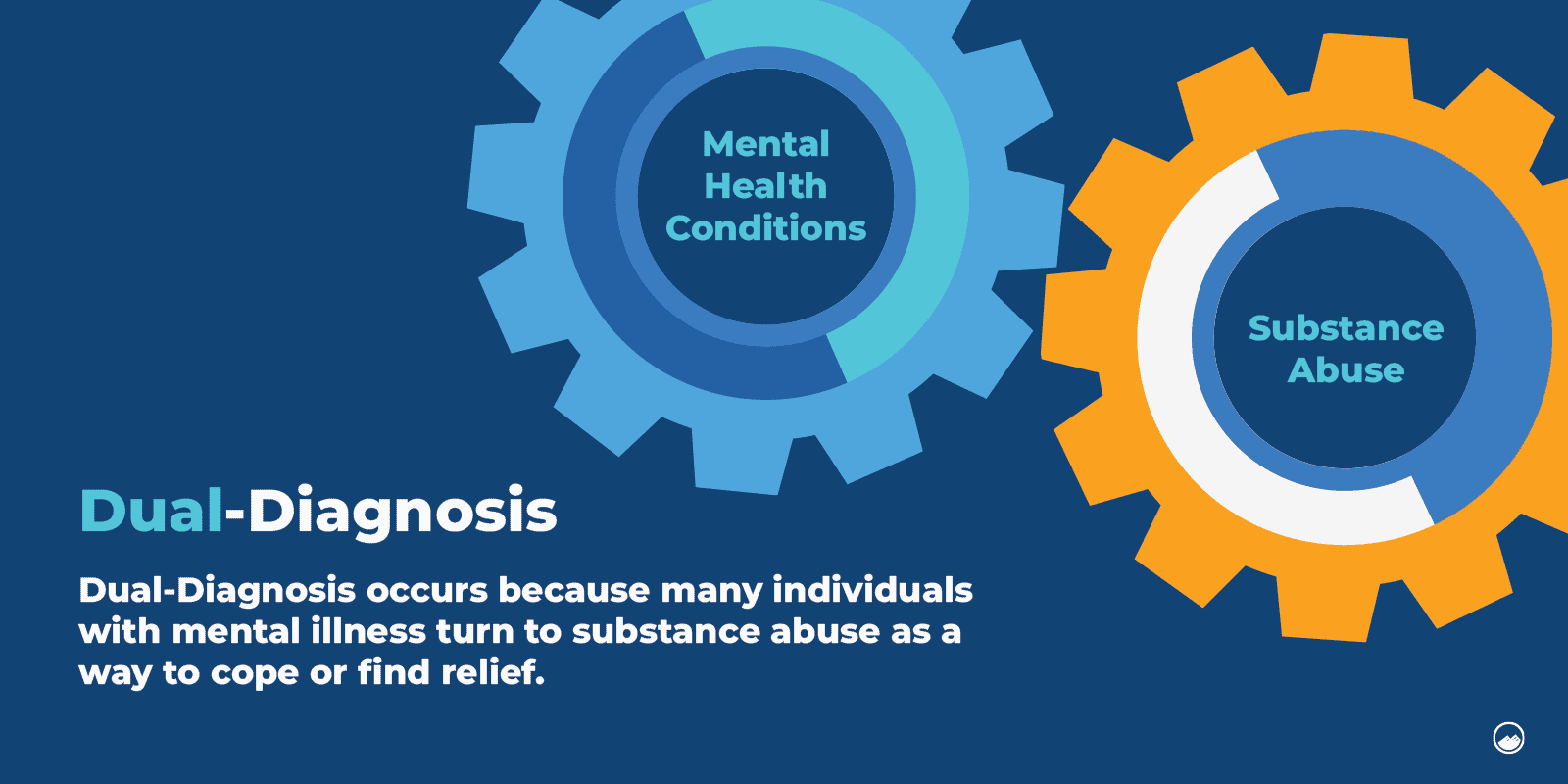
The relationship between mental health conditions and substance use is complex. Many individuals with mental illnesses turn to substance abuse as a way to cope or find relief. This co-occurrence, known as dual diagnosis, requires professional mental health support for effective recovery.
Mental illness and behavioral health issues increase the risk of drug use and risky behaviors. Individuals with mental health conditions may seek out drugs or engage in substance abuse as a means of self-medication. Addressing mental health concerns is vital in preventing and managing substance abuse.
Understanding the connection between mental health and substance use is crucial for developing effective strategies. By providing comprehensive care that addresses both aspects, we can improve outcomes and promote healthier coping mechanisms.
Access to quality substance use treatment is vital for individuals struggling with addiction. Healthcare providers, including mental health professionals, play a crucial role in guiding individuals toward effective treatment programs. These programs provide the necessary support and resources to help individuals overcome substance use disorders and achieve lasting recovery.
One essential component of substance use treatment is medication-assisted treatment (MAT). MAT combines medication, such as methadone or buprenorphine, with counseling and behavioral therapies. This comprehensive approach is effective in managing withdrawal symptoms, reducing cravings, and preventing relapse.
Treatment centers play a significant role in providing a safe and supportive environment for individuals seeking help for substance use. These centers offer various treatment modalities, including individual therapy, group counseling, and educational programs, tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual.


We understand taking the first step is difficult. There is no shame or guilt in asking for help or more information. We are here to support you in any way we can.