Dual Diagnosis Meaning
What is Dual Diagnosis?
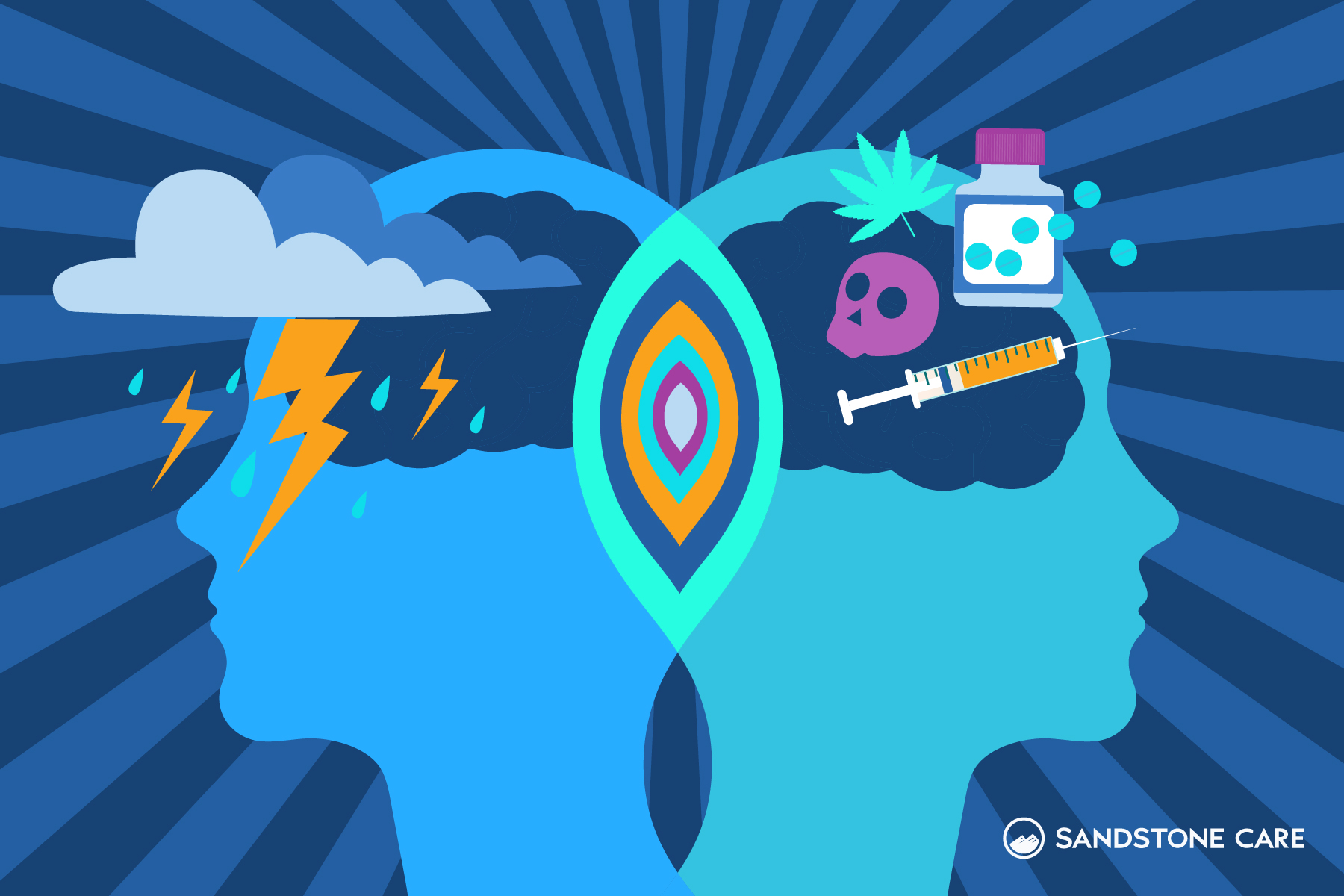
Dual diagnosis is a term used to describe when someone has both a substance use disorder (SUD) and a mental illness.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) explains that more than one in four adults with a severe mental illness also experience substance use. Some data suggest this number is even higher, closer to one in two.
Some mental health problems are more closely associated with developing a SUD, such as:
- Depression and other mood disorders
- Anxiety disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Personality disorders
- ADHD
Dual diagnosis highlights how substance use and mental health disorders affect each other. For example, someone with severe anxiety may self-medicate with alcohol to cope. Or chronic drug use may trigger depression, psychosis, or other psychiatric disorders.
What Are Co-Occurring Disorders?
A co-occurring disorder is another term for a dual diagnosis. Examples include:
- Anxiety disorders: Someone with severe anxiety who abuses alcohol to cope
- Bipolar disorders: An individual with bipolar disorder who self-medicates with opioids and becomes addicted
- Schizophrenia: Someone who has schizophrenia and relies on stimulants.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder: A trauma survivor who has post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and uses heavy drinking to cope
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) explains how these conditions are often treated together because of their overlapping risk factors. Trauma, genetics, environment, and personal chemistry all play a role in one’s mental health.
What is a Dual Diagnosis Program?
A dual diagnosis treatment program addresses both substance use disorders and other mental health conditions simultaneously.
These programs may incorporate several forms of care, such as:
- Detoxification
- Psychotherapy
- Behavioral therapy
- Peer Support
Depending on the severity of your condition and your personal needs, outpatient, inpatient, or partial hospitalization treatment programs are potential options.
Sandstone Care has several programs that offer dual diagnosis treatment plans for teens, young adults, and adults. Call (888) 850-1890 for more information on how to enroll.
Why Go to a Dual Diagnosis Rehab
What Are the Benefits of Dual Diagnosis?
The main benefit of a dual diagnosis rehab facility is their understanding that mental health disorders and substance abuse affect each other. They focus on both.
A dual diagnosis program may provide:
- A comprehensive treatment plan addressing both conditions
- Evidence-based therapies, including medication and counseling options
- Support groups and peer support communities with others who also have dual diagnoses
- Reduced substance use and a better chance of recovery for both SUD and mental health conditions
- Reduced medication interactions due to coordinated care across fewer providers
- Improved quality of life and functioning
- Housing stability
How Do Substance Use and Mental Health Affect Each Other?
Substance use and mental health affect each other because those with high levels of mental distress may be at a greater risk of relapse from their substance use disorder.
Depression: For example, someone with depression and anxiety may drink to cope with their symptoms. However, alcohol is a depressant and can worsen depression symptoms.
Anxiety: Additionally, while those with anxiety may experience a temporary decrease in symptoms, alcohol can lead to impulsivity and affect sleep. This can negatively affect anxiety in the long term.
Those with more serious mental illness, which is characterized by poorer psychological functioning and higher levels of mental distress, are more likely to experience substance abuse problems.
The severity of mental health symptoms, combined with the greater likelihood of relapse, is what makes dual diagnosis treatment essential.
Without treating the mental health disorders adequately, an individual may be more likely to relapse. And without treating the SUD, therapy for a mental health disorder may not be as effective.
Can Dual Diagnosis Detox Programs Help with Withdrawal Symptoms?
Absolutely! Dual diagnosis detox programs can help with withdrawal symptoms—for many, detoxification, or detox for short, is the first stage of recovery.
Specialized dual diagnosis detox programs provide medical supervision for detox as well as psychiatric care and medications for co-occurring conditions.
Withdrawal symptoms may worsen underlying mental health disorders, such as anxiety. Dual diagnosis programs are equipped to handle how the conditions affect each other.
Examples of Dual Diagnosis
What Are Examples of Co-occurring Disorders?
There are several examples of co-occurring conditions seen in dual diagnoses, including, but not limited to:
- Depression and alcohol use disorder
- Anxiety disorders and sedative misuse
- Bipolar disorder and cannabis use disorder
- Schizophrenia and cannabis use disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and alcohol use disorder
- ADHD and stimulant drug abuse
Depression and Alcohol Addiction
Depression and alcohol addiction are one of the most common dual diagnoses.
The co-occurrence of alcohol abuse and depression often leads to more severe symptoms for both and worse outcomes.
While those with alcohol use disorder may turn to alcohol to cope, alcohol is a depressant and can worsen depressive symptoms. It also affects neurotransmitters in the brain and reduces the effectiveness of medications for depression.
ADHD and Stimulant Use
Those with ADHD are at a higher risk of developing a SUD, particularly with stimulants, and ADHD is a common co-occurring condition.
Over 10% of individuals with a SUD may also have ADHD.
While many with ADHD are prescribed stimulants as treatment and use them safely, there is also the risk of abuse. Those with ADHD may also misuse recreational stimulants, such as cocaine or methamphetamine.
In one study, 45% of people who misused cocaine and methamphetamines had ADHD symptoms. Other studies have found varying rates, ranging from 10% to over 20%.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment Centers
What Should I Look for in a Dual Diagnosis Therapist?
Look for a dual diagnosis therapist who:
- Is licensed in mental health treatment and has additional training in addiction counseling
- Uses evidence-based methods, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Involves family members (as appropriate) and peer or support groups in recovery
- Provides patient education on the warning signs of a relapse and what to do if symptoms begin to worsen
- Assists in discharge planning to help ensure things like stable housing and basic resources
- Collaborates with other members of the care team, such as psychiatrists, nurses, case managers, and other treatment providers.
This list is not exhaustive, and you may need different traits depending on your needs.
What Does Integrated Treatment Look Like?
Integrated treatment looks like addressing both SUD and co-occurring mental health conditions simultaneously.
Integrated care is often the best treatment approach as it may reduce the severity of mental health symptoms and the rate of relapse.
Integrated treatment programs often include:
- Detoxification with medical support
- Behavioral therapies that address multiple conditions
- Medication management for both substance use problems and other co-existing mental illnesses
- Psychotherapy to address trauma, build coping skills, and help prevent relapse
- Peer-support groups
- Case management that can assist with housing, employment, accessing food, and legal aid
Treatment can occur at an inpatient care facility for acute stabilization or through outpatient programming, such as intensive outpatient or partial hospitalization programs.
Residential facilities also exist for those who are no longer detoxing but still require a higher level of around-the-clock support before transitioning to an outpatient program.
How Do I Find a Dual Diagnosis Treatment Center?
There are several ways to find the right treatment center. Individuals may locate facilities on their own or through referrals from another provider.
Ways to find help include:
- Using the SAMHSA Helpline
- Seeking referrals from a primary care provider, mental health provider, or therapist
- Asking peers for recommendations on treatment centers
- Reaching out to organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) for peer support recommendations
If cost is an issue, non-profit or community-based programs may offer more affordable treatment options.
Sandstone Care is here to help and offers dual diagnosis programs led by trained clinicians. Treatment is available in both residential and outpatient settings. Call (888) 850-1890.